

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 9 [PDF Available]
- Updated on
- December 6, 2024

Reported speech exercises for class 9: In this vast realm of English Grammar , reported speech , commonly known as indirect speech, plays an important role in conveying information relayed from another person. However, for class 9 students, grasping the nuances of reported speech is essential for effective communication and comprehension. The blog article below aims to provide class 9 students with engaging exercises to solidify their preparation.
This Blog Includes:
What is reported speech, reported speech rules to know, quiz for reported speech exercises for class 9, exercise 1: change direct speech to reported speech, exercise 2: choose the correct reported speech, exercise 3: create reported speech, exercise 4: fill in the blanks with the appropriate reported speech, exercise 5: convert sentences to indirect speech, exercise 6: change into reported speech, exercise 7: convert sentences to indirect speech, exercise 8: complete the sentences to reported speech.
Oxford Learner’s Dictionary definition of reported speech is “ A report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” As per the Macmillan Dictionary, the words that you use to report what someone else has said are known are reported speech.
Check out some examples of reported speech to get a basic idea:
- Direct Speech: “I like pizza,” she said.
- Reported Speech: She said she liked pizza.
- Direct Speech: “We will go to the beach tomorrow,” they said.
- Reported Speech: They said they would go to the beach the next day.
MUST READ! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples, Tips, Exercises for Students
Here are some common rules for changing direct speech to reported speech:
➡️ We use conjunctions like ‘if’, and ‘whether’ after the reporting verb in reported speech
➡️ The reporting verb’s tense is never altered.
➡️ The verb of reporting varies according to sense: it can be told, inquired, asked, etc.
➡️ First and foremost, we do not use inverted commas in reported speech which must be clear from the example given above.
Also Read: Useful Idioms for IELTS Exams That Will Boost Your Score
Here’s a quiz on reported speech for students. Each question presents a direct speech statement, and you need to rewrite it in reported speech. Choose the correct option for each question.
Question 1: Direct Speech: “I love playing the guitar.”
a) He loves playing the guitar. b) I love playing the guitar. c) He loved playing the guitar. d) I loved playing the guitar.
Question 2: Direct Speech: “We are going to the park tomorrow.”
a) They are going to the park tomorrow. b) We were going to the park tomorrow. c) They were going to the park tomorrow. d) We go to the park tomorrow.
Question 3: Direct Speech: “She said, ‘I have already finished my homework.'”
a) She said that she already finished her homework. b) She said that she had already finished her homework. c) She says that she finished her homework already. d) She said that she has already finished her homework.
Question 4: Direct Speech: “The teacher exclaimed, ‘What a wonderful painting!'”
a) The teacher exclaimed that it was a wonderful painting. b) The teacher exclaimed what a wonderful painting it was. c) The teacher exclaimed that what a wonderful painting. d) The teacher exclaimed a wonderful painting.
Question 5: Direct Speech: “I will call you later.”
a) He said that he will call you later. b) He said that he would call you later. c) He says that he will call you later. d) He says that he would call you later.
Question 6: Direct Speech: “They said, ‘We haven’t received the email.'”
a) They said that they haven’t received the email. b) They said that they didn’t receive the email. c) They said that they hadn’t received the email. d) They say that they haven’t received the email.
Question 7: Direct Speech: “Tom said, ‘I can swim.'”
a) Tom said that he could swim. b) Tom says that he could swim. c) Tom said that he can swim. d) Tom says that he can swim.
- b) I love playing the guitar.
- a) They are going to the park tomorrow.
- b) She said that she had already finished her homework.
- b) The teacher exclaimed what a wonderful painting it was.
- b) He said that he would call you later.
- c) They said that they hadn’t received the email.
- a) Tom said that he could swim.
Also Read: 50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Interrogative Sentences
Following are some useful reported speech exercises for class 9. Convert the following sentences from direct speech to reported speech:
Direct Speech : She said, “I am going to the store.”
Reported Speech : She said that she was going to the store.
Direct Speech : He said, “I will finish the project by Friday.”
Reported Speech : He said that he would finish the project by Friday.
Direct Speech : “We have completed our homework,” they said.
Reported Speech : They said that they had completed their homework.
Direct Speech : “They are coming to the party,” she said.
Reported Speech : She said that they were coming to the party.
Direct Speech : “I can speak French,” he said.
Reported Speech : He said that he could speak French.
Read the following sentences and choose the correct reported speech option:
Direct Speech : “I saw Sarah yesterday,” Tom said.
a) Tom said he had seen Sarah yesterday.
b) Tom said he sees Sarah yesterday.
Correct Answer: a) Tom said he had seen Sarah yesterday.
Direct Speech : “I’m going to the cinema tonight,” she said.
a) She said she was going to the cinema that night.
b) She said she is going to the cinema tonight.
Correct Answer: a) She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct Speech : “We will travel to Paris next week,” they said.
a) They said they will travel to Paris next week.
b) They said they would travel to Paris the following week.
Correct Answer: b) They said they would travel to Paris the following week.
Direct Speech : “I have finished my work,” he said.
a) He said he has finished his work.
b) He said he had finished his work.
Correct Answer: b) He said he had finished his work.
Direct Speech : “I’m cooking dinner right now,” she said.
a) She said she was cooking dinner right then.
b) She said she is cooking dinner right now.
Correct Answer: a) She said she was cooking dinner right then.
Must Read: Subject-Verb Agreement: Definition, 12 Rules & Examples
Form reported speech for the following direct speech sentences:
Direct Speech : “She will be here soon,” he said.
Reported Speech : He mentioned that she would be there soon.
Direct Speech : “I don’t like seafood,” she said.
Reported Speech : She expressed that she didn’t like seafood.
Direct Speech : “They were studying in the library,” he said.
Reported Speech : He mentioned that they had been studying in the library.
Direct Speech : “I am working on a new project,” she said.
Reported Speech : She mentioned that she was working on a new project.
Direct Speech : “We have completed the assignment,” they said.
Reported Speech : They confirmed that they had completed the assignment.
Also Read: Tenses Rules: Charts, Examples, Types [PDF Available]
Practise the following direct sentences to appropriate report speech.
She said, “I have been to Paris before.”
Reported Speech : She mentioned that she had been to Paris before.
“We will come early,” they said.
Reported Speech : They said that they would come early.
“He’s writing a novel,” she said.
Reported Speech : She mentioned that he was writing a novel.
“I won’t be able to attend the meeting,” he said.
Reported Speech : He said that he wouldn’t be able to attend the meeting.
“We were watching a movie,” they said.
Reported Speech : They mentioned that they had been watching a movie.
Also Read: Adjective: Definition, Usage, Example, Forms, Types
Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
- He said, “Honesty is the best policy.”
- He said, “The sun rises in the east.”
- Rakesh said, “I am an early riser.”
- She said, “God is omnipresent.”
- The teacher said, “The First World War started in 1914.”
Check Answers :
1. He said that honesty was the best policy.
2. He said that the sun rises in the east.
3. Rakesh said that he was an early riser.
4. She said that God is omnipresent.
5. The teacher said that the First World War had started in 1914.
Exploring the Types of Reported Speech: A Complete Guide
Read the following sentences and convert them into reported speech.
- Rahul said, “I get up early every morning.”
- Andrew said, “I can do this work.”
- Priya said, “It is hot outside.”
- Raj said to Marie, “I will go to London tomorrow.”
- Archie said to me, “I will cook today’s dinner.”
Check Your Answers:
- Rahul said that he got up early every morning.
- Andrew said that he could do that work.
- Priya said that it was hot outside.
- Raj informed Marie that he would go to London the next day.
- Archie said to me that he would cook that day’s dinner.
Must Read: Reported Speech For Class 10: Exciting Exercises with Answers [PDF]
Convert the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech.
- Direct Speech: “I love playing basketball,” said Sarah.
- Direct Speech: “We are going to visit Paris next month,” said Tom.
- Direct Speech: “She has already finished her homework,” said Jack.
- Direct Speech: “They will arrive at 9 o’clock,” said the receptionist.
- Direct Speech: “I have never been to Japan,” said Emily.
- Sarah said that she loved playing basketball.
- Tom said that they were going to visit Paris the following month.
- Jack said that she had already finished her homework.
- The receptionist said that they would arrive at 9 o’clock.
- Emily said that she had never been to Japan.
Reported speech is a way of conveying what someone said without directly quoting their exact words. It involves changing the original sentence’s structure, tense, and pronouns to fit the new context.
Reported speech exercises help reinforce understanding of how to report what someone else has said. They aid in learning how to shift verb tenses, pronouns, time expressions, and other changes when reporting speech.
When converting direct speech to reported speech, pay attention to the changes in verb tenses, pronouns, time expressions, and other relevant modifications based on the context and the tense used in the original sentence.
Common changes include the shift of tenses (present to past, future to conditional), pronoun changes, changes in time expressions (today to that day, tomorrow to the next day), and changes in modal verbs (can to could, will to would, etc.).
Universal Truths: These remain unchanged. Example: Direct: “The Earth revolves around the Sun.” Indirect: He said that the Earth revolves around the Sun. Specific Tenses: Sometimes, the original tense is retained if it’s still relevant to the present context.
To report orders, use verbs like ‘ordered’, ‘commanded’, ‘instructed’. Example: Direct: “Close the door!” Indirect: He ordered me to close the door. To report requests, use verbs like ‘requested’, ‘asked’, ‘begged’. Example: Direct: “Please help me.” Indirect: He requested me to help him.
Time and place references often change to reflect the new context. Now becomes then Today becomes that day Yesterday becomes the previous day Tomorrow becomes the next day Here becomes there This becomes that
We hope this blog has provided you with all the necessary information on reported speech exercises for class 9 . To advance your grammar knowledge and read more informative blogs, check out our Learn English page and don’t forget to follow Leverage Edu .
Vaishnavi Shukla
Vaishnavi has 2+ years of experience in SEO and Content Marketing. She is highly proficient in English, possessing exceptional language skills and a deep understanding of English grammar and communication. Currently working on Ed Tech, Finance, Lifestyle, and other niches. All her works are infused with love for writing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2025
January 2026
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

CBSE Class 9 English Reported Speech Notes
Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 9 English Reported Speech Notes. Students and teachers of Class 9 English can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 9 English prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school. Class 9 students should download this study material which will give them more knowledge for all chapters in English and all important topics which are scoring and can get you more marks. Students should also download free pdf of Chapter wise Notes for Class 9 English prepared by school teachers as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, KVS books and syllabus issued this year and also download free worksheets and question papers available here to get higher scores in school exams and tests, also click here for more Study Material for Class 9 English

Study Material for Class 9 English Reported Speech
Class 9 English students should refer to the following Pdf for Reported Speech in Class 9. These notes and test paper with questions and answers for Class 9 English will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Class 9 English Reported Speech
We can express thing spoken or told by others in 2 ways.
- To speak what the speaker said as it is - Direct Speech
- To express what the speaker said in our own words -Indirect Speech
If you ask your friend – “Where is your book”, the reply could be –“Your book is with Sam”.
Now, if I ask you, what did your friend tell you, then you can narrate that in 2 ways.
- He said to me, “your book is with Sam”. -Direct Narration.
- My friend told me that your book was with Sam. -Indirect Narration.
RULES TO CHANGE FROM DIRECT TO INDIRECT SPEECH:
- Remove the inverted commas. (“………..”)
- Remove the full stop or comma after the reporting verb.
- If there is any object after the reporting verb then change’ said to’ to ‘told’ &’say ‘to ‘tell’.
- If there is no object after the reporting verb then no change in ‘said’ and ‘say’.
- Add necessary conjunction like ‘that, if, whether’ after the reporting verb.
(a) Changes in the Tense of Reported Speech (R.S.) :
if the reporting verb (R.V.) is in present or Future Tense, there is no change in the tense of R.S.
She says, “He is not here”. (Direct)
She says that he is not here (Indirect)
She will say, ”Tom drives a car”. (Direct)
She will say that Tom drives a car. (Indirect)
If R.V is in Past tense, then of R.S is changed as follows:
Simple present is changed into Simple Past.
John said to Jim, “Sam studies regularly”. (Direct)
John told Jim that Sam studied regularly. (Indirect)
Present Continuous is changed to Past Continuous.
Chappell said to Sachin, “Dravid is playing football”. (Direct)
Chappell told Sachin, the “Dravid was playing football”. (Indirect)
Present perfect is changed to past perfect.
Dhoni said, ”Pathan has gone to West Indies”. (Direct)
Dhoni said that Pathan had gone to West Indies”. (Indirect)
Present perfect Continuous is changed to past perfect Continuous.
My neighbour said, “The dogs have been braking for 2 hours”. (Direct)
My neighbour said that dogs had been braking for 2 hours”. (Indirect)
Simple past is changed to past perfect.
John said,” Jim went to U.S.A.” (Direct)
John said that Jim had gone to U.S.A. (Indirect)
Past continuous is changed to past perfect continuous.
She said, “Her sister was sleeping”. (Direct)
She said that her sister had been sleeping. (Indirect)
No changes in past perfect and past perfect continuous.
Papa said,” Johnny had eaten sugar”. (Direct)
Papa said that Johnny had eaten sugar. (Indirect)
Change in modals:
Can changes to could; May changes to should; will to would;
The principal said,” Student can go home”. (Direct)
The principal said that Student could go home. (Indirect)
Would, Should, Could, Might, Ought – do not change.
Must can be changed to ‘had to’ or used as it is.
We said, “The criminals must be punished”. (Direct)
We said that the criminals had to /must be punished”. (Indirect)
(b) Exceptions:
Historical Facts : Sir said,”Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India”. (Direct)
Sir said that Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India. (Indirect)
Universal Truth : The teacher said,” Sun rises in the East”. (Direct)
The teacher said that the Sun rises in the East”. (Indirect)
Habitual Facts : The Doctor said.” Smoking is injurious to health”. (Direct)
The Doctor said that Smoking is injurious to health”. (In direct)
(c) Changes in persons of pronoun:
(i) First person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us. our, ours ,ourselves)in the R.V. when changed into indirect speech, change as per the person, Number andGender of the Subject of R.V.
They said, “We shall help our friends”. (Direct)
They said that the would help their friends. (Indirect)
(ii) Second person pronoun(you, you, yours, yourself, yourselves) in the R.V. when changed into indirect speech, change as per the person, Number andGender of the Subject of the Object.
She said to us, “You are intelligent”. (Direct)
She said to us that we are intelligent. (Indirect)
The teacher said to the student, “You” have passed with good marks”. (Direct)
The teacher told the student that they had passed with good marks. (Indirect)
No change in the Third Person Pronoun (He, She, It, They, Her, Its, Their, Theirs,Him, Himself, Herself, Themselves, Her, Hers)when changed from Direct into Indirect Speech.
- Greg said, “She is a good student”. (Direct)
- Greg said that She was a good student. (Indirect)
(d) Change of Situations :
‘this becomes ‘that’
‘these’ becomes ‘those’
‘least week’ becomes ‘the previous week’
‘here’ becomes ‘there’
‘now’ becomes ‘then’
‘today’ becomes ‘that day’
‘yesterday’ becomes ‘the day before/the previous day’
tomorrow’ becomes ‘the next day/ the coming day’
‘lest week’ becomes ‘the week before/the previous week’
‘next month’ becomes ‘the week before/the previous week’
‘ago’ becomes ‘before’
Jacob said, “I read this book last month.” (Direct)
Jacob said that he had read that book the previous month (Indirect)
Mary said, “I will meet Tom this evening” (Direct)
Mary said that she would meet Tom this evening (Indirect)
Marshall said to Ricky.” I cannot go with you till next Monday” (Direct)
Marshall said to Ricky.” I cannot go with you till next Monday” (Indirect )
(e) Imperative Situations :
Write “Ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded, Forbade ”etc. as per the sentences.
The teacher said to me, “sit in your class and learn your lesson” (Direct)
The teacher ordered me to sit in my class and learn my lesson. (Indirect)
She said to him, ”Don’t touch my books” (Direct)
She forbade him to touch her books. (Indirect)
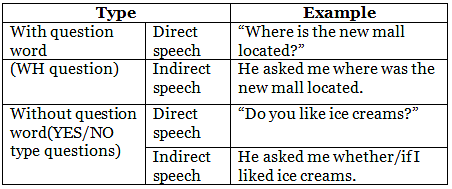
(f) Interrogative Sentences :
(i) For ‘wh’ question – use the wh word
Tim asked, “Where is the book ?” (Direct)
Tim asked Where the book was. ( Indirect)
(ii) For yes /No question – use if / whether
Surabhi asked, “Have you read this book?” (Direct)
Surabhi asked if whether I had read that book.
Question. Keshav said, “Rita is busy right now.” a) Keshav said Rita was busy. b) Keshav informed that Rita was busy then. c) Keshav said Rita had been busy. d) Keshav informed that Rita is busy.
Question. Rahul said, “I will manage hereafter.” a) Rahul said that he would manage hereafter. b) Rahul said that he will manage thereafter. c) Rahul said that he would manage thereafter. d) Rahul said that he will manage hereafter.
Question. She said, “Bring a glass of water, please.” a) She commands me to bring a glass of water. b) She requested me to bring a glass of water. c) She asked me to brought a glass of water. d) She ordered me to bring her a glass of water.
Question. She said, “They will be leaving soon.” a) She said that they would leave soon. b) She said that they are leaving. c) She said that they would be leaving soon. d) She said that they will leave soon.
Question. The policeman said, “Don’t cross the speed limit.” a) The policeman said not to cross the speed limit. b) The policeman asked if I would cross the speed limit. c) The policeman forbade me to cross the speed limit. d) The policeman asks if I had crossed the speed limit.
Question. He said, “Ah! You are here.” a) He exclaimed with delight that I was there. b) He said that he was delighted that I was there. c) He exclaimed with joy to see me there. d) He said it was a joy to see me there.
Question. “Don’t make noise in the library.” the librarian said. a) The librarian said not to make noise in the library. b) The librarian ordered me not to make noise in the library. c) The librarian said to be quiet while in the library. d) The librarian asks me to not make any noise.
Question. Jacob said, “Have you read this book?” a) Jacob asked me if I have read this book. b) Jacob asked me if I had read that book. c) Jacob asked me if I would read this book. d) Jacob asked me if I had been reading this book.
Question. The lawyer said, “The law always believes in the evidence.” a) The lawyer said that the law always believed in the evidence. b) The lawyer said that the law should always believe in the evidence. c) The lawyer said that the law always believes in the evidence. d) The lawyer said that the law has always believed in the evidence.
Question. “Wow! This is so beautiful.” Jacob said. a) Jacob was surprised to see how beautiful it was. b) Jacob said how beautiful it was. c) Jacob exclaimed with amazement that that was so beautiful. d) Jacob exclaimed with amazement that it was so beautiful.
Question. Meera said, “It’s time. I must go now.” a) Meera said that it is time and she should leave. b) Meera said that it was time and she had to go then. c) Meera said that it was time to go then. d) Meera said it is time and she may go.
Question. He said that he would deposit the cheque the following day. a) He said, “I will deposit the cheque the next day.” b) He said, “I would deposit the cheque soon.” c) He said, “I will deposit the cheque tomorrow.” d) He said, “I would deposit the cheque the following day.”
Question. He said that he had been looking for the file. a) He said, “I am looking for the file.” b) He said, “I was looking for the file.” c) He said, “I have looked for the file.” d) He said, “I have been looking for the file.”
Question. He said that he would not go with us. a) He said, “I will not go with you all.” b) He said, “I will not go with them.” c) He said, “I would not go with them.” d) He said, “I will not be going with them.”
Question. He said that I had to reach early. a) He said, “You shall reach early.” b) He said, “You should reach early.” c) He said to me, “Reach early.” d) He said, “You must reach early.”
Question. Natasha pleaded to her mother to let her buy a black dress. a) Natasha pleaded to her mother, “Let me buy a black dress.” b) Natasha pleaded to her mother, “Let us buy a black dress.” c) Natasha pleaded to her mother, “I need to buy a black dress.” d) Natasha pleaded to her mother, “We should a balck dress.”
Question. Henry exclaimed with regret that he had missed his flight. a) Henry said, “Alas! I miss my flight.” b) Henry said, “I missed my flight.” c) Henry said, “Oh! I missed my flight.” d) Henry said, “I would miss my flight!”
Question. Keshav said that he had been watching a movie. a) Keshav said, “I have watched this movie.” b) Keshav said. “I would be watching a movie.” c) Keshav said, “I should watch a movie.” d) Keshav said, “I have been watching a movie.”
Question. He said that the grandmother would be visiting. a) He said, “The grandmother will visit.” b) He said, “The grandmother shall visit.” c) He said, “The grandmother must be visiting.” d) He said, “The grandmother may be visiting.”
Question. The head said to the staff that they had thought of a solution. a) The head said, “We have a solution.” b) The head said to the staff, “We have thought of a solution!” c) The head said to the staff, “We have thought of a solution.” d) The head said, “We have been thinking of a solution.”
Question. Kiara said that she had been planning for that for a while. a) Kiara said, “I had a plan for this for a while.” b) Kiara said, “I have planned for this for a while.” c) Kiara said, “I have been planning for this for a while.” d) Kiara said, “I planned this for a while.”
Question. Tim said, “I may teach you if you will show sincerity.” a) Tim said that he might teach me if I would show sincerity. b) Tim said that he may teach me at a condition. c) Tim said that he could teach me had I shown sincerity. d) Tim said that he will teach me if I was to show sincerity.
Question. He said that Chris had been busy. a) He said, “Chris is busy.” b) He said, “Chris was busy.” c) He said, “Chris had been busy.” d) He said, “Chris have been busy.”
Question. The teacher quoted that slow and steady wins the race. a) The teacher said, “Slow and steady should win the race.” b) The teacher said, “Slow and steady have won the race.” c) The teacher said, “Slow and steady have been winning the race.” d) The teacher said, “Slow and steady wins the race.”
Question. She informed me that he had met with a road accident. a) She said to me, “He met with a road accident.” b) She said to me, “Alas! He meets with a road accident.” c) She said to me, “Has he met with a road accident?” d) She said to me, “He did meet with a road accident.”
CBSE Class 9 English Reported Speech Study Material
We hope students liked the above Study Material for Reported Speech designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 9 English released by CBSE. Students of Class 9 should download the Study Material in Pdf format, read the notes and related questions and solutions given in above Class 9 English Study Material on daily basis. All latest Study Material have been developed for English by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 9 English to develop the English Class 9 Study Material. After solving the questions given in the Study Material which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 9 English designed by our teachers. Also download Class 9 English Sample Papers given on studiestoday. After solving these you should also refer to Class 9 English MCQ Test for the same chapter.
You can download free study material for Class 9 English Reported Speech for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the study material given here for Class 9 English Reported Speech is for current CBSE session
All study maetrial for CBSE Class 9 English Reported Speech is free
- Tue. Dec 24th, 2024
English Syllabus Guru
Your Ultimate English Syllabus Learning Resource
Reported Speech Rules and Exercises Pdf
By Waqas Sharif

Practice Reported speech Rules and Exercises by downloading this Pdf. Reported speech is also known as the direct and indirect narration in English. It refers to when we report or repeat what someone has said, without directly quoting them. The following are some of the main rules in English grammar for forming reported speech:
- Timeshift: When converting direct speech to reported speech, the verb tense often needs to be changed to reflect the difference in time between the original speech and the reporting of it.
- Pronouns shift: Pronouns in direct speech may need to be changed in reported speech, to reflect the relationship between the speaker and the person being quoted.
- Modal verbs shift: Modal verbs in direct speech may need to be changed in a reported speech to reflect the speaker’s attitude or degree of certainty about what was said.
- Reporting verbs: Reporting verbs , such as “say,” “tell,” and “ask,” are used to introduce reported speech.
- Reporting clauses: Reporting clauses, such as “that,” “if,” and “whether,” are used to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
Note: It’s important to keep in mind the purpose of the reported speech and the relationship between the speaker and the person being quoted.
Download Reported Speech Pdf Below
Share this:.

Mr. Waqas Sharif is an English Language Teaching (ELT) Professional, Trainer, and Course Instructor at a Public Sector Institute. He has more than ten years of Eng Language Teaching experience at the Graduate and Postgraduate level. His main interest is found in facilitating his students globally He wishes them to develop academic skills like Reading, Writing, and Communication mastery along with Basics of Functional Grammar, English Language, and Linguistics.
Related Post
Speed reading tips: how to read faster and recall more, 10 days to faster reading by abbymarks beale, on writing well, the classic guide to writing nonfiction pdf, leave a reply cancel reply, writing tools: 55 essential strategies for every writer.
Reported Speech | English Grammar for Class 9 PDF Download
How to change Exclamatory Sentences into Indirect Speech? :
- Reporting verb SAID / SAID TO should be changed into EXCLAIMED.
- Use the conjunction word THAT.
- Change that into a Statement.
- When WHAT or HOW is followed by an adjective, use VERY but when WHAT is followed by a noun use GREAT.
- HOW is usually followed by an Adjective (not by a Noun).
- Change of Personal Pronoun, Tense and Special words.
- Remove commas, quotation marks and exclamation mark.
Formula : Subject + exclaimed + that + other subject (from Reported Speech) + verb (by changing the tense) + very + adjective (or great + noun)+ …. Examples :
- They said, “Hurrah! We have won the match”. They exclaimed joyfully that they had won the match.
- She said, “What a tall building!” She exclaimed joyfully that it was a tall building.
Interrogative Sentences
When turning questions into indirect speech, we have to pay attention to the following points:
- As in a declarative sentence, we have to change the pronouns and the time and place information, and set back the tense (backshift).
- Instead of that (as in a declarative sentence), we use the question word. If there is no question word, we use whether/if instead.
- Besides this, we also need to use an indirect question in indirect speech. This means that after the question word or after whether/if, we simply write a declarative sentence (subject-verb etc.).
Changing the Tense (backshift)
If the introductory verb is in the simple past (e.g. He said), the tense has to be set back by one degree . The term for this in English is backshift.
- He said, “I check my mail every day.” He said that he checked his mail every day.
- He said, “I saw a new film.” He said that he had seen a new film.
- He said, “She was studying when you were plaing.” He said that she had been studying where I was playing.
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn’t, ought to, used to normally do not change.
- He said, “I could have asked her for an autograph.”
- He said that he could have asked her for an autograph.
No Change of Tenses
If the introductory verb is in the simple present, however (e.g. He says), then the tense remains unchanged, because the introductory clause already indicates that the statement is being immediately repeated (and not at a later point in time). Example:
- He says, “I saw a new film.”
- He says that he saw a new film.
In some cases, however, we have to change the verb form.
- She says, “I read every day.”
- She says that she reads every day.
- He says, “She was reading when you are playing.”
- He says that she was reading when I was playing.
Top Courses for Class 9
Extra questions, reported speech | english grammar for class 9, past year papers, study material, objective type questions, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, video lectures, shortcuts and tricks, semester notes, practice quizzes, mock tests for examination, viva questions, sample paper.

Reported Speech Free PDF Download
Importance of reported speech, reported speech notes, reported speech class 9 questions, study reported speech on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Lesson 9. Reported Speech Reporting Statements –Tenses 2. Tenses If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported speech. If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported speech. Backshift You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e. g. He said).
DIRECT SPEECH REPORTED SPEECH *The above examples also depend on where the reported statement is being made. For example, if the above reported statements are being made while the person reporting the information is still in the same place where the conversation took place, the reported speech could also be: Kevin asked if I had been here before.
Dec 6, 2024 · Quiz for Reported Speech Exercises for Class 9. Here’s a quiz on reported speech for students. Each question presents a direct speech statement, and you need to rewrite it in reported speech. Choose the correct option for each question. Question 1: Direct Speech: “I love playing the guitar.” a) He loves playing the guitar.
ENGLISH GRAMMAR Reported Speech 3 All those changes represent the distancing effect of the reported speech. Common sense, together with the time aspect from the speaker’s point of view, are more important than the rules when making the usual changes. QUESTIONS IN INDIRECT SPEECH Direct question: He said, “Where is she going?”
Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 9 English Reported Speech Notes. Students and teachers of Class 9 English can get free advanced study material, revision notes, sure shot questions and answers for Class 9 English prepared as per the latest syllabus and examination guidelines in your school.
Feb 6, 2022 · * Interrogative sentences beginning with an auxiliary verb, (can, are, has, have, do etc.) are changed into the indirect speech, by using the connective if or whether., , * The reporting verb said (or any other word used as the, reporting verb) changes to asked, questioned, or enquired of in, the indirect speech.
Feb 8, 2023 · Practice Reported speech Rules and Exercises by downloading this Pdf. Reported speech is also known as the direct and indirect narration in English. It refers to when we report or repeat what someone has said, without directly quoting them. The following are some of the main rules in English grammar for forming reported speech:
77 REPORTED SPEECH 1. Read the conversation between a young boy and his mother. The boy is determined to go to camp, despite his mother's refusal to let him (from George Layfon's short story "The Holiday"). It wasn't fair. Tony and Barry were going. In fact, nearly all of them in Class Three and Four were going, except me. It wasn't fair.
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Reported Speech | English Grammar for Class 9 - Class 9 | Plus excerises question with solution to help you revise complete syllabus for English Grammar for Class 9 | Best notes, free PDF download
Feb 5, 2022 · Page 2 : She says, “My dad likes roast chicken.” – She says that her dad likes roast chicken., Tenses, , , , If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported, speech., If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported, speech., Direct speech, , , , Reported speech, , (no backshift) “I write poems.”