Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to's, java reference, java examples, java arrays.
Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable, instead of declaring separate variables for each value.
To declare an array, define the variable type with square brackets :
We have now declared a variable that holds an array of strings. To insert values to it, you can place the values in a comma-separated list, inside curly braces:
To create an array of integers, you could write:

Access the Elements of an Array
You can access an array element by referring to the index number.
This statement accesses the value of the first element in cars:
Try it Yourself »
Note: Array indexes start with 0: [0] is the first element. [1] is the second element, etc.
Change an Array Element
To change the value of a specific element, refer to the index number:
Array Length
To find out how many elements an array has, use the length property:

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
Java Arrays
Java strings.
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
Java Multithreading
Java exception handling.
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
Arrays in Java
Arrays are fundamental structures in Java that allow us to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. They are useful for managing collections of data efficiently. Arrays in Java work differently than they do in C/C++. This article covers the basics and in-depth explanations with examples of array declaration , creation , and manipulation in Java.
Arrays are fundamental to Java programming. They allow you to store and manipulate collections of data efficiently. If you’re looking to get hands-on with more complex array operations and learn advanced techniques, the Java Programming Course offers a structured approach to mastering arrays in Java.
Let us start with an example of to print the elements of an Array:
Table of Content
Basics of Arrays in Java
Creating, initializing, and accessing an arrays in java, types of arrays in java, 1. single-dimensional arrays, 2. multi-dimensional arrays, arrays of objects in java, multidimensional arrays in java.
There are some basic operations we can start with as mentioned below:
1. Array Declaration
To declare an array in Java, use the following syntax:
type[] arrayName;
- type : The data type of the array elements (e.g., int , String ).
- arrayName : The name of the array.
Note: The array is not yet initialized.
2. Create an Array
To create an array, you need to allocate memory for it using the new keyword :
// Creating an array of 5 integers numbers = new int[5];
This statement initializes the numbers array to hold 5 integers. The default value for each element is 0 .
3. Access an Element of an Array
We can access array elements using their index, which starts from 0 :
// Setting the first element of the array numbers[0] = 10; // Accessing the first element int firstElement = numbers[0];
The first line sets the value of the first element to 10 . The second line retrieves the value of the first element.
4. Change an Array Element
To change an element, assign a new value to a specific index:
// Changing the first element to 20 numbers[0] = 20;
5. Array Length
We can get the length of an array using the length property:
// Getting the length of the array int length = numbers.length;
Now, we have completed with basic operations so let us go through the in-depth concepts of Java Arrays , through the diagrams, examples, and explanations.
In-Depth Concepts of Java Array
Following are some important points about Java arrays.
Array Properties
- In Java, all arrays are dynamically allocated .
- Arrays may be stored in contiguous memory [consecutive memory locations].
- Since arrays are objects in Java, we can find their length using the object property length . This is different from C/C++, where we find length using size of.
- A Java array variable can also be declared like other variables with [] after the data type.
- The variables in the array are ordered, and each has an index beginning with 0.
- Java array can also be used as a static field, a local variable, or a method parameter.
An array can contain primitives (int, char, etc.) and object (or non-primitive) references of a class, depending on the definition of the array. In the case of primitive data types, the actual values might be stored in contiguous memory locations (JVM does not guarantee this behavior). In the case of class objects, the actual objects are stored in a heap segment .

Note: This storage of arrays helps us randomly access the elements of an array [Support Random Access].
For understanding the array we need to understand how it actually works. To understand this follow the flow mentioned below:
i. Declaring an Array
The general form of array declaration is
Method 1: type var-name[]; Method 2: type[] var-name;
The element type determines the data type of each element that comprises the array. Like an array of integers, we can also create an array of other primitive data types like char, float, double, etc., or user-defined data types (objects of a class).
Note: It is just how we can create is an array variable, no actual array exists . It merely tells the compiler that this variable (int Array) will hold an array of the integer type.
Now, Let us provide memory storage to this created array.
ii. Initialization an Array in Java
When an array is declared, only a reference of an array is created. The general form of new as it applies to one-dimensional arrays appears as follows:
var-name = new type [size];
Here, type specifies the type of data being allocated, size determines the number of elements in the array, and var-name is the name of the array variable that is linked to the array. To use new to allocate an array, you must specify the type and number of elements to allocate.
Example:
// declaring array int intArray[]; // allocating memory to array intArray = new int[20]; // combining both statements in one int[] intArray = new int[20];
Note: The elements in the array allocated by new will automatically be initialized to zero (for numeric types), false (for boolean), or null (for reference types). Do refer to default array values in Java .
Obtaining an array is a two-step process. First, you must declare a variable of the desired array type. Second, you must allocate the memory to hold the array, using new, and assign it to the array variable. Thus, in Java , all arrays are dynamically allocated.
Array Literal in Java
In a situation where the size of the array and variables of the array are already known, array literals can be used.
// Declaring array literal int[] intArray = new int[]{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
- The length of this array determines the length of the created array.
- There is no need to write the new int[] part in the latest versions of Java.
iii. Accessing Java Array Elements using for Loop
Now , we have created an Array with or without the values stored in it. Access becomes an important part to operate over the values mentioned within the array indexes using the points mentioned below:
- Each element in the array is accessed via its index.
- The index begins with 0 and ends at (total array size)-1.
- All the elements of array can be accessed using Java for Loop.
Let us check the syntax of basic for loop to traverse an array:
// Accessing the elements of the specified array for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) System.out.println(“Element at index ” + i + ” : “+ arr[i]);
Implementation:
Java supports different types of arrays:
These are the most common type of arrays, where elements are stored in a linear order.
// A single-dimensional array int[] singleDimArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};

Arrays with more than one dimension, such as two-dimensional arrays (matrices).
// A 2D array (matrix) int[][] multiDimArray = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9} };
You can also access java arrays using for each loops .
An array of objects is created like an array of primitive-type data items in the following way.
Method 1: ObjectType[] arrName; Method 2: ObjectType arrName[];
Example of Arrays of Objects
Example 1: Here we are taking a student class and creating an array of Student with five Student objects stored in the array. The Student objects have to be instantiated using the constructor of the Student class, and their references should be assigned to the array elements.
Example 2: An array of objects is also created like
What happens if we try to access elements outside the array size?
JVM throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException to indicate that the array has been accessed with an illegal index. The index is either negative or greater than or equal to the size of an array.
Below code shows what happens if we try to access elements outside the array size:
Multidimensional arrays are arrays of arrays with each element of the array holding the reference of other arrays. These are also known as Jagged Arrays . A multidimensional array is created by appending one set of square brackets ([]) per dimension.
There are 2 methods to declare Java Multidimensional Arrays as mentioned below:
// Method 1 datatype [][] arrayrefvariable; // Method 2 datatype arrayrefvariable[][];

Declaration:
// 2D array or matrix int[][] intArray = new int[10][20]; // 3D array int[][][] intArray = new int[10][20][10];
Java Multidimensional Arrays Examples
Example 1: Let us start with basic two dimensional Array declared and initialized.
Example 2: Now, after declaring and initializing the array we will check how to Traverse the Multidimensional Array using for loop.
Passing Arrays to Methods
Like variables, we can also pass arrays to methods. For example, the below program passes the array to method sum to calculate the sum of the array’s values.
Returning Arrays from Methods
As usual, a method can also return an array. For example, the below program returns an array from method m1 .
Java Array Members
Now, as you know that arrays are objects of a class, and a direct superclass of arrays is a class Object.
The members of an array type are all of the following:
- The public final field length contains the number of components of the array. Length may be positive or zero.
- All the members are inherited from class Object; the only method of Object that is not inherited is its clone method.
- The public method clone() overrides the clone method in class Object and throws no checked exceptions .
Arrays Types and Their Allowed Element Types
Cloning arrays in java, 1. cloning of single-dimensional array.
When you clone a single-dimensional array, such as Object[] , a shallow copy is performed. This means that the new array contains references to the original array’s elements rather than copies of the objects themselves. A deep copy occurs only with arrays containing primitive data types, where the actual values are copied.

Below is the implementation of the above method:
2. Cloning Multidimensional Array
A clone of a multi-dimensional array (like Object[][]) is a “shallow copy,” however, which is to say that it creates only a single new array with each element array a reference to an original element array, but subarrays are shared.

Advantages of Java Arrays
- Efficient Access : Accessing an element by its index is fast and has constant time complexity, O(1).
- Memory Management : Arrays have fixed size, which makes memory management straightforward and predictable.
- Data Organization : Arrays help organize data in a structured manner, making it easier to manage related elements.
Disadvantages of Java Arrays
- Fixed Size : Once an array is created, its size cannot be changed, which can lead to memory waste if the size is overestimated or insufficient storage if underestimated.
- Type Homogeneity : Arrays can only store elements of the same data type, which may require additional handling for mixed types of data.
- Insertion and Deletion : Inserting or deleting elements, especially in the middle of an array, can be costly as it may require shifting elements.
M ust Read:
Jagged Array in Java For-each loop in Java Arrays class in Java
Frequently Asked Questions – Java Arrays
How can we initialize an array in java.
Arrays in Java can be initialized in several ways: Static Initialization : int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; Dynamic Initialization : int[] arr = new int[5]; Initialization with a loop : for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = i + 1; }
Can we use an array of primitive types in Java?
Yes, Java supports arrays of primitive types such as int , char , boolean , etc., as well as arrays of objects.
How are multidimensional arrays represented in Java?
Multidimensional arrays in Java are represented as arrays of arrays. For example, a two-dimensional array is declared as int[][] array , and it is effectively an array where each element is another array.
Can we change the size of an array after it is created in Java?
No, the size of an array in Java cannot be changed once it is initialized. Arrays are fixed-size. To work with a dynamically sized collection, consider using classes from the java.util package, such as ArrayList .
Can we specify the size of an array as long in Java?
No, we cannot specify the size of an array as long . The size of an array must be specified as an int . If a larger size is required, it must be handled using collections or other data structures.
What is the direct superclass of an array in Java?
The direct superclass of an array in Java is Object . Arrays inherit methods from the Object class, including toString() , equals() , and hashCode() .
Which interfaces are implemented by arrays in Java?
All arrays in Java implement two interfaces: Cloneable : Allows the array to be cloned using the clone() method. java.io.Serializable : Enables arrays to be serialized.
Similar Reads
- Java Tutorial Java is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages which is used to develop mobile apps, desktop apps, web apps, web servers, games, and enterprise-level systems. Java was invented by James Gosling and Oracle currently owns it. JDK 23 is the latest version of Java. Popular platfor 4 min read
Java Overview
- Introduction to Java Java is a class-based, object-oriented programming language that is designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is intended to let application developers Write Once and Run Anywhere (WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the 10 min read
- The Complete History of Java Programming Language Java is an Object-Oriented programming language developed by James Gosling in the early 1990s. The team initiated this project to develop a language for digital devices such as set-top boxes, television, etc. Originally C++ was considered to be used in the project but the idea was rejected for sever 5 min read
- How to Download and Install Java for 64 bit machine? Java is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages. It is a simple, portable, platform-independent language. It has been one of the most popular programming languages for many years. In this article, We will see How to download and install Java for Windows 64-bit. We'll also be an 4 min read
- Setting up the environment in Java Java is a general-purpose computer programming language that is concurrent, class-based, object-oriented, etc. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of computer architecture. The latest version is Java 22. Below are the environ 6 min read
- How JVM Works - JVM Architecture JVM(Java Virtual Machine) runs Java applications as a run-time engine. JVM is the one that calls the main method present in a Java code. JVM is a part of JRE(Java Runtime Environment). Java applications are called WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere). This means a programmer can develop Java code on one s 7 min read
- JDK in Java The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a cross-platformed software development environment that offers a collection of tools and libraries necessary for developing Java-based software applications and applets. It is a core package used in Java, along with the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and the JRE (Java 5 min read
- Differences between JDK, JRE and JVM Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment used for developing Java applications and applets. It includes the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), an interpreter/loader (Java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (Javadoc), and other tools needed in Java 5 min read
Java Basics
- Java Syntax Java is an object-oriented programming language which is known for its simplicity, portability, and robustness. The syntax of Java programming language is very closely aligned with C and C++ which makes it easier to understand. Let's understand the Syntax and Structure of Java Programs with a basic 5 min read
- Java Hello World Program Java is one of the most popular and widely used programming languages and platforms. Java is fast, reliable, and secure. Java is used in every nook and corner from desktop to web applications, scientific supercomputers to gaming consoles, cell phones to the Internet. In this article, we will learn h 5 min read
- Java Identifiers An identifier in Java is the name given to Variables, Classes, Methods, Packages, Interfaces, etc. These are the unique names and every Java Variables must be identified with unique names. Example: public class Test{ public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 20; }}In the above Java code, we h 2 min read
- Java Keywords In Java, Keywords or Reserved words are the words in a language that are used for some internal process or represent some predefined actions. These words are therefore not allowed to use as variable names or objects. If we do we will get a compile-time error as shown below as follows: Example of Jav 5 min read
- Java Data Types Java is statically typed and also a strongly typed language because, in Java, each type of data (such as integer, character, hexadecimal, packed decimal, and so forth) is predefined as part of the programming language and all constants or variables defined for a given program must be described with 11 min read
- Java Variables Variables are the containers for storing the data values or you can also call it a memory location name for the data. Every variable has a: Data Type - The kind of data that it can hold. For example, int, string, float, char, etc.Variable Name - To identify the variable uniquely within the scope.Val 8 min read
- Scope of Variables In Java Scope of a variable is the part of the program where the variable is accessible. Like C/C++, in Java, all identifiers are lexically (or statically) scoped, i.e.scope of a variable can be determined at compile time and independent of function call stack. Java programs are organized in the form of cla 5 min read
- Operators in Java Java provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need. They are classified based on the functionality they provide. In this article, we will learn about Java Operators and learn all their types. What are the Java Operators?Operators in Java are the symbols used for performing 15 min read
- How to Take Input From User in Java? Java brings various Streams with its I/O package that helps the user perform all the Java input-output operations. These streams support all types of objects, data types, characters, files, etc. to fully execute the I/O operations. Input in Java can be with certain methods mentioned below in the art 5 min read
Java Flow Control
- Java if statement The Java if statement is the most simple decision-making statement. It is used to decide whether a certain statement or block of statements will be executed or not i.e. if a certain condition is true then a block of statements is executed otherwise not. Example: [GFGTABS] Java // Java program to ill 5 min read
- Java if-else Decision-making in Java helps to write decision-driven statements and execute a particular set of code based on certain conditions. The if statement alone tells us that if a condition is true it will execute a block of statements and if the condition is false it won’t. In this article, we will learn 3 min read
- Java if-else-if ladder with Examples Decision Making in Java helps to write decision-driven statements and execute a particular set of code based on certain conditions.Java if-else-if ladder is used to decide among multiple options. The if statements are executed from the top down. As soon as one of the conditions controlling the if is 3 min read
- For Loop in Java Loops in Java come into use when we need to repeatedly execute a block of statements. Java for loop provides a concise way of writing the loop structure. The for statement consumes the initialization, condition, and increment/decrement in one line thereby providing a shorter, easy-to-debug structure 7 min read
- For-each loop in Java The for-each loop in Java (also called the enhanced for loop) was introduced in Java 5 to simplify iteration over arrays and collections. It is cleaner and more readable than the traditional for loop and is commonly used when the exact index of an element is not required. Example: Below is a basic e 6 min read
- Java while Loop Java while loop is a control flow statement used to execute the block of statements repeatedly until the given condition evaluates to false. Once the condition becomes false, the line immediately after the loop in the program is executed. Let's go through a simple example of a Java while loop: [GFGT 3 min read
- Java Do While Loop Java do-while loop is an Exit control loop. Unlike for or while loop, a do-while check for the condition after executing the statements of the loop body. Example: [GFGTABS] Java // Java program to show the use of do while loop public class GFG { public static void main(String[] args) { int c = 1; // 4 min read
- Break statement in Java Break Statement is a loop control statement that is used to terminate the loop. As soon as the break statement is encountered from within a loop, the loop iterations stop there, and control returns from the loop immediately to the first statement after the loop. Syntax: break;Basically, break state 3 min read
- Continue Statement in Java Suppose a person wants code to execute for the values as per the code is designed to be executed but forcefully the same user wants to skip out the execution for which code should have been executed as designed above but will not as per the demand of the user. In simpler words, it is a decision-maki 6 min read
- return keyword in Java In Java, return is a reserved keyword i.e., we can't use it as an identifier. It is used to exit from a method, with or without a value. Usage of return keyword as there exist two ways as listed below as follows: Case 1: Methods returning a valueCase 2: Methods not returning a valueLet us illustrat 6 min read
Java Methods
- Java Methods The method in Java or Methods of Java is a collection of statements that perform some specific tasks and return the result to the caller. A Java method can perform some specific tasks without returning anything. Java Methods allows us to reuse the code without retyping the code. In Java, every metho 10 min read
- How to Call Method in Java Java Methods are the collection of statements used for performing certain tasks and for returning the end result to the user.Java Methods enables the reuse the code without retyping the code. Every class in Java has its own methods, either inherited methods or user-defined methods that are used to d 4 min read
- Static methods vs Instance methods in Java In this article, we are going to learn about Static Methods and Instance Methods in Java. Java Instance MethodsInstance methods are methods that require an object of its class to be created before it can be called. To invoke an instance method, we have to create an Object of the class in which the m 5 min read
- Access Modifiers in Java in Java, Access modifiers help to restrict the scope of a class, constructor, variable, method, or data member. It provides security, accessibility, etc to the user depending upon the access modifier used with the element. Let us learn about Java Access Modifiers, their types, and the uses of access 6 min read
- Command Line Arguments in Java Java command-line argument is an argument i.e. passed at the time of running the Java program. In Java, the command line arguments passed from the console can be received in the Java program and they can be used as input. The users can pass the arguments during the execution bypassing the command-li 3 min read
- Variable Arguments (Varargs) in Java Variable Arguments (Varargs) in Java is a method that takes a variable number of arguments. Variable Arguments in Java simplifies the creation of methods that need to take a variable number of arguments. Need of Java VarargsUntil JDK 4, we cant declare a method with variable no. of arguments. If the 4 min read
- Arrays in Java Arrays are fundamental structures in Java that allow us to store multiple values of the same type in a single variable. They are useful for managing collections of data efficiently. Arrays in Java work differently than they do in C/C++. This article covers the basics and in-depth explanations with e 15+ min read
- How to Initialize an Array in Java? An array in Java is a data structure used to store multiple values of the same data type. Each element in an array has a unique index value. It makes it easy to access individual elements. In an array, we have to declare its size first because the size of the array is fixed. In an array, we can stor 6 min read
- Java Multi-Dimensional Arrays A multidimensional array can be defined as an array of arrays. Data in multidimensional arrays are stored in tabular form (row-major order). Example: [GFGTABS] Java // Java Program to Demonstrate // Multi Dimensional Array import java.io.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) 9 min read
- Jagged Array in Java Prerequisite: Arrays in Java A jagged array is an array of arrays such that member arrays can be of different sizes, i.e., we can create a 2-D array but with a variable number of columns in each row. These types of arrays are also known as Jagged arrays. Pictorial representation of Jagged array in M 5 min read
- Arrays class in Java The Arrays class in java.util package is a part of the Java Collection Framework. This class provides static methods to dynamically create and access Java arrays. It consists of only static methods and the methods of Object class. The methods of this class can be used by the class name itself. The c 13 min read
- Final Arrays in Java As we all know final variable declared can only be initialized once whereas the reference variable once declared final can never be reassigned as it will start referring to another object which makes usage of the final impracticable. But note here that with final we are bound not to refer to another 4 min read
- Strings in Java In Java, a String is an object that represents a sequence of characters. Java provides a robust and flexible API for handling strings, allowing for various operations such as concatenation, comparison, and manipulation. In this article, we will go through the Java String concept in detail. What are 9 min read
- Why Java Strings are Immutable? Before proceeding further with the fuss of immutability, let's just take a look into the String class and its functionality a little before coming to any conclusion. In this article, we will learn about the fact why Java Strings are Immutable. What are Immutable objects?Immutable objects are objects 5 min read
- Java String concat() Method with Examples The string concat() method concatenates (appends) a string to the end of another string. It returns the combined string. It is used for string concatenation in Java. It returns NullPointerException if any one of the strings is Null. In this article, we will learn how to concatenate two strings in Ja 4 min read
- String class in Java String is a sequence of characters. In Java, objects of the String class are immutable which means they cannot be changed once created. In this article, we will learn about the String class in Java. Example of String Class in Java: [GFGTABS] Java // Java Program to Create a String import java.io.*; 7 min read
- StringBuffer class in Java StringBuffer is a class in Java that represents a mutable sequence of characters. It provides an alternative to the immutable String class, allowing you to modify the contents of a string without creating a new object every time. Here are some important features and methods of the StringBuffer class 13 min read
- StringBuilder Class in Java with Examples StringBuilder in Java represents a mutable sequence of characters. Since the String Class in Java creates an immutable sequence of characters, the StringBuilder class provides an alternative to String Class, as it creates a mutable sequence of characters. The function of StringBuilder is very much s 6 min read
- String vs StringBuilder vs StringBuffer in Java A string is a sequence of characters. In Java, objects of String are immutable which means a constant and cannot be changed once created. Initializing a String is one of the important pillars required as a pre-requisite with deeper understanding. Comparison between String, StringBuilder, and StringB 7 min read
Java OOPs Concepts
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concept in Java As the name suggests, Object-Oriented Programming or Java OOPs concept refers to languages that use objects in programming, they use objects as a primary source to implement what is to happen in the code. Objects are seen by the viewer or user, performing tasks you assign. Object-oriented programmin 12 min read
- Classes and Objects in Java In Java, classes and objects are basic concepts of Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) that are used to represent real-world concepts and entities. The class represents a group of objects having similar properties and behavior. For example, the animal type Dog is a class while a particular dog named 11 min read
- Java Constructors Java constructors or constructors in Java is a terminology used to construct something in our programs. A constructor in Java is a special method that is used to initialize objects. The constructor is called when an object of a class is created. It can be used to set initial values for object attrib 8 min read
- Object Class in Java Object class is present in java.lang package. Every class in Java is directly or indirectly derived from the Object class. If a class does not extend any other class then it is a direct child class of Object and if extends another class then it is indirectly derived. Therefore the Object class metho 7 min read
- Abstraction in Java Abstraction in Java is the process in which we only show essential details/functionality to the user. The non-essential implementation details are not displayed to the user. In this article, we will learn about abstraction and what abstraction means. Simple Example to understand Abstraction:Televisi 11 min read
- Encapsulation in Java Encapsulation in Java is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that refers to the bundling of data and methods that operate on that data within a single unit, which is called a class in Java. Java Encapsulation is a way of hiding the implementation details of a class from outsid 8 min read
- Inheritance in Java Java, Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object-Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in Java by which one class is allowed to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class. In Java, Inheritance means creating new classes based on existing ones. A class that inherits from ano 13 min read
- Polymorphism in Java The word 'polymorphism' means 'having many forms'. In simple words, we can define Java Polymorphism as the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form. In this article, we will learn what is polymorphism and its type. Real-life Illustration of Polymorphism in Java: A person can have d 6 min read
- Method Overloading in Java In Java, Method Overloading allows different methods to have the same name, but different signatures where the signature can differ by the number of input parameters or type of input parameters, or a mixture of both. Method overloading in Java is also known as Compile-time Polymorphism, Static Polym 9 min read
- Overriding in Java In Java, Overriding is a feature that allows a subclass or child class to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already provided by one of its super-classes or parent classes. When a method in a subclass has the same name, the same parameters or signature, and the same return type(or 13 min read
- Packages In Java Package in Java is a mechanism to encapsulate a group of classes, sub packages and interfaces. Packages are used for: Preventing naming conflicts. For example there can be two classes with name Employee in two packages, college.staff.cse.Employee and college.staff.ee.EmployeeMaking searching/locatin 8 min read
Java Interfaces
- Interfaces in Java An Interface in Java programming language is defined as an abstract type used to specify the behavior of a class. An interface in Java is a blueprint of a behavior. A Java interface contains static constants and abstract methods. What are Interfaces in Java?The interface in Java is a mechanism to ac 11 min read
- Interfaces and Inheritance in Java A class can extend another class and can implement one and more than one Java interface. Also, this topic has a major influence on the concept of Java and Multiple Inheritance. Note: This Hierarchy will be followed in the same way, we cannot reverse the hierarchy while inheritance in Java. This mean 7 min read
- Differences between Interface and Class in Java This article highlights the differences between a class and an interface in Java. They seem syntactically similar, both containing methods and variables, but they are different in many aspects. Differences between a Class and an Interface The following table lists all the major differences between a 4 min read
- Functional Interfaces in Java Java has forever remained an Object-Oriented Programming language. By object-oriented programming language, we can declare that everything present in the Java programming language rotates throughout the Objects, except for some of the primitive data types and primitive methods for integrity and simp 10 min read
- Nested Interface in Java We can declare interfaces as members of a class or another interface. Such an interface is called a member interface or nested interface. Interfaces declared outside any class can have only public and default (package-private) access specifiers. In Java, nested interfaces (interfaces declared inside 5 min read
- Marker interface in Java It is an empty interface (no field or methods). Examples of marker interface are Serializable, Cloneable and Remote interface. All these interfaces are empty interfaces. public interface Serializable { // nothing here } Examples of Marker Interface which are used in real-time applications : Cloneabl 3 min read
- Comparator Interface in Java with Examples A comparator interface is used to order the objects of user-defined classes. A comparator object is capable of comparing two objects of the same class. Following function compare obj1 with obj2. Syntax: public int compare(Object obj1, Object obj2):Suppose we have an Array/ArrayList of our own class 6 min read
Java Collections
- Collections in Java Any group of individual objects that are represented as a single unit is known as a Java Collection of Objects. In Java, a separate framework named the "Collection Framework" has been defined in JDK 1.2 which holds all the Java Collection Classes and Interface in it. In Java, the Collection interfac 15+ min read
- Collections Class in Java Collections class in Java is one of the utility classes in Java Collections Framework. The java.util package contains the Collections class in Java. Java Collections class is used with the static methods that operate on the collections or return the collection. All the methods of this class throw th 14 min read
- Collection Interface in Java with Examples The Collection interface is a member of the Java Collections Framework. It is a part of java.util package. It is one of the root interfaces of the Collection Hierarchy. The Collection interface is not directly implemented by any class. However, it is implemented indirectly via its subtypes or subint 8 min read
- Java List Interface The List Interface in Java extends the Collection Interface and is a part of java.util package. It is used to store the ordered collections of elements. So in a Java List, you can organize and manage the data sequentially. Maintained the order of elements in which they are added.Allows the duplicate 15+ min read
- ArrayList in Java Java ArrayList is a part of collections framework and it is a class of java.util package. It provides us with dynamic arrays in Java. Though, it may be slower than standard arrays but can be helpful in programs where lots of manipulation in array is required. The main advantage of ArrayList is, unli 10 min read
- Vector Class in Java The Vector class implements a growable array of objects. Vectors fall in legacy classes, but now it is fully compatible with collections. It is found in java.util package and implement the List interface. Thread-Safe: All methods are synchronized, making it suitable for multi-threaded environments. 13 min read
- LinkedList in Java Linked List is a part of the Collection framework present in java.util package. This class is an implementation of the LinkedList data structure which is a linear data structure where the elements are not stored in contiguous locations and every element is a separate object with a data part and addr 13 min read
- Stack Class in Java Java Collection framework provides a Stack class that models and implements a Stack data structure. The class is based on the basic principle of LIFO(last-in-first-out). In addition to the basic push and pop operations, the class provides three more functions of empty, search, and peek. The Stack cl 11 min read
- Set in Java The Set Interface is present in java.util package and extends the Collection interface. It is an unordered collection of objects in which duplicate values cannot be stored. It is an interface that implements the mathematical set. This interface adds a feature that restricts the insertion of the dupl 14 min read
- Java HashSet HashSet in Java implements the Set interface of Collections Framework. It is used to store the unique elements and it doesn't maintain any specific order of elements. Can store the Null values.Uses HashTable internally.Also implements Serializable and Cloneable interfaces.HashSet is not thread-safe. 12 min read
- TreeSet in Java TreeSet is one of the most important implementations of the SortedSet interface in Java that uses a Tree(red - black tree) for storage. The ordering of the elements is maintained by a set using their natural ordering whether or not an explicit comparator is provided. This must be consistent with equ 13 min read
- LinkedHashSet in Java with Examples Let us start with a simple Java code snippet that demonstrates how to create a LinkedHashSet object without adding any elements to it: [GFGTABS] Java import java.util.LinkedHashSet; public class LinkedHashSetCreation { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a LinkedHashSet of Strings Lin 9 min read
- Queue Interface In Java The Queue Interface is present in java.util package and extends the Collection interface. It stores and processes the data in FIFO(First In First Out) order. It is an ordered list of objects limited to inserting elements at the end of the list and deleting elements from the start of the list. No Nul 13 min read
- PriorityQueue in Java The PriorityQueue class in Java is part of the java.util package. It is known that a Queue follows the FIFO(First-In-First-Out) Algorithm, but the elements of the Queue are needed to be processed according to the priority, that's when the PriorityQueue comes into play. The PriorityQueue is based on 11 min read
- Deque interface in Java with Example Deque Interface present in java.util package is a subtype of the queue interface. The Deque is related to the double-ended queue that supports adding or removing elements from either end of the data structure. It can either be used as a queue(first-in-first-out/FIFO) or as a stack(last-in-first-out/ 10 min read
- Map Interface in Java In Java, Map Interface is present in java.util package represents a mapping between a key and a value. Java Map interface is not a subtype of the Collection interface. Therefore it behaves a bit differently from the rest of the collection types. No Duplicates in Keys: Ensures that keys are unique. H 12 min read
- HashMap in Java In Java, HashMap is part of the Java Collections Framework and is found in the java.util package. It provides the basic implementation of the Map interface in Java. HashMap stores data in (key, value) pairs. Each key is associated with a value, and you can access the value by using the corresponding 15+ min read
- LinkedHashMap in Java Let us start with a simple Java code snippet that demonstrates how to create and use a LinkedHashMap in Java. [GFGTABS] Java import java.util.LinkedHashMap; public class LinkedHashMapCreation { public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a LinkedHashMap of Strings (keys) and Integers (values) 9 min read
- Hashtable in Java Let us start with a simple Java code snippet that demonstrates how to create and use a HashTable. [GFGTABS] Java import java.util.Hashtable; public class HashtableCreation { public static void main(String args[]) { // Create a Hashtable of String keys and Integer values Hashtable<String, Integer 14 min read
- Java.util.Dictionary Class in Java The java.util.Dictionary class in Java is an abstract class that represents a collection of key-value pairs, where keys are unique and are used to access the values. It was part of the Java Collections Framework introduced in Java 1.2 but has been largely replaced by the java.util.Map interface sinc 7 min read
- SortedSet Interface in Java with Examples The SortedSet interface is present in java.util package extends the Set interface present in the collection framework. It is an interface that implements the mathematical set. This interface contains the methods inherited from the Set interface and adds a feature that stores all the elements in this 8 min read
- Comparable Interface in Java with Examples The Comparable interface is used to compare an object of the same class with an instance of that class, it provides ordering of data for objects of the user-defined class. The class has to implement the java.lang.Comparable interface to compare its instance, it provides the compareTo method that tak 4 min read
- Comparable vs Comparator in Java Java provides two interfaces to sort objects using data members of the class: ComparableComparatorUsing Comparable Interface A comparable object is capable of comparing itself with another object. The class itself must implements the java.lang.Comparable interface to compare its instances. Consider 6 min read
- Iterators in Java A Java Cursor is an Iterator, that is used to iterate or traverse or retrieve a Collection or Stream object’s elements one by one. In this article, we will learn about Java Iterators and it's working. Types of Cursors in JavaThere are three cursors in Java as mentioned below: IteratorEnumerationList 14 min read
- Exceptions in Java Exception Handling in Java is one of the effective means to handle runtime errors so that the regular flow of the application can be preserved. Java Exception Handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors such as ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, RemoteException, etc. What are Ja 10 min read
- Checked vs Unchecked Exceptions in Java In Java, Exception is an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program, i.e. at run time, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions. In Java, there are two types of exceptions: Checked exceptionsUnchecked exceptions Understanding the difference betwee 5 min read
- Java Try Catch Block In Java exception is an "unwanted or unexpected event", that occurs during the execution of the program. When an exception occurs, the execution of the program gets terminated. To avoid these termination conditions we can use try catch block in Java. In this article, we will learn about Try, catch, 4 min read
- final, finally and finalize in Java This is an important question concerning the interview point of view. final keyword final (lowercase) is a reserved keyword in java. We can't use it as an identifier, as it is reserved. We can use this keyword with variables, methods, and also with classes. The final keyword in java has a different 13 min read
- throw and throws in Java In Java, Exception Handling is one of the effective means to handle runtime errors so that the regular flow of the application can be preserved. Java Exception Handling is a mechanism to handle runtime errors such as NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, etc. In this article, we will 4 min read
- User-defined Custom Exception in Java An exception is an issue (run time error) that occurred during the execution of a program. When an exception occurred the program gets terminated abruptly and, the code past the line that generated the exception never gets executed. Java provides us the facility to create our own exceptions which ar 3 min read
- Chained Exceptions in Java Chained Exceptions allows to relate one exception with another exception, i.e one exception describes cause of another exception. For example, consider a situation in which a method throws an ArithmeticException because of an attempt to divide by zero but the actual cause of exception was an I/O err 3 min read
- Null Pointer Exception In Java NullPointerException is a RuntimeException. In Java, a special null value can be assigned to an object reference. NullPointerException is thrown when a program attempts to use an object reference that has the null value. Reason for Null Pointer ExceptionThese are certain reasons for Null Pointer Exc 6 min read
- Exception Handling with Method Overriding in Java An Exception is an unwanted or unexpected event, which occurs during the execution of a program i.e at run-time, that disrupts the normal flow of the program’s instructions. Exception handling is used to handle runtime errors. It helps to maintain the normal flow of the program. In any object-orient 6 min read
- Java Multithreading Tutorial Threads are the backbone of multithreading. We are living in a real world which in itself is caught on the web surrounded by lots of applications. With the advancement in technologies, we cannot achieve the speed required to run them simultaneously unless we introduce the concept of multi-tasking ef 15+ min read
- Java Threads Typically, we can define threads as a subprocess with lightweight with the smallest unit of processes and also has separate paths of execution. The main advantage of multiple threads is efficiency (allowing multiple things at the same time). For example, in MS Word. one thread automatically formats 9 min read
- Java.lang.Thread Class in Java Thread is a line of execution within a program. Each program can have multiple associated threads. Each thread has a priority which is used by the thread scheduler to determine which thread must run first. Java provides a thread class that has various method calls in order to manage the behavior of 8 min read
- Runnable interface in Java java.lang.Runnable is an interface that is to be implemented by a class whose instances are intended to be executed by a thread. There are two ways to start a new Thread - Subclass Thread and implement Runnable. There is no need of subclassing a Thread when a task can be done by overriding only run( 3 min read
- Lifecycle and States of a Thread in Java A thread in Java at any point of time exists in any one of the following states. A thread lies only in one of the shown states at any instant: New StateRunnable StateBlocked StateWaiting StateTimed Waiting StateTerminated StateThe diagram shown below represents various states of a thread at any inst 6 min read
- Main thread in Java Java provides built-in support for multithreaded programming. A multi-threaded program contains two or more parts that can run concurrently. Each part of such a program is called a thread, and each thread defines a separate path of execution.When a Java program starts up, one thread begins running i 4 min read
- Java Thread Priority in Multithreading As we already know java being completely object-oriented works within a multithreading environment in which thread scheduler assigns the processor to a thread based on the priority of thread. Whenever we create a thread in Java, it always has some priority assigned to it. Priority can either be give 5 min read
- Naming a thread and fetching name of current thread in Java Thread can be referred to as a lightweight process. Thread uses fewer resources to create and exist in the process; thread shares process resources. The main thread of Java is the thread that is started when the program starts. now let us discuss the eccentric concept of with what ways we can name a 5 min read
- Difference between Thread.start() and Thread.run() in Java In Java's multi-threading concept, start() and run() are the two most important methods. Below are some of the differences between the Thread.start() and Thread.run() methods: New Thread creation: When a program calls the start() method, a new thread is created and then the run() method is executed. 3 min read
- Thread.sleep() Method in Java With Examples Thread Class is a class that is basically a thread of execution of the programs. It is present in Java.lang package. Thread class contains the Sleep() method. There are two overloaded methods of Sleep() method present in Thread Class, one is with one argument and another one is with two arguments. T 4 min read
- Daemon Thread in Java In Java, daemon threads are low-priority threads that run in the background to perform tasks such as garbage collection or provide services to user threads. The life of a daemon thread depends on the mercy of user threads, meaning that when all user threads finish their execution, the Java Virtual M 4 min read
- Thread Safety and how to achieve it in Java As we know Java has a feature, Multithreading, which is a process of running multiple threads simultaneously. When multiple threads are working on the same data, and the value of our data is changing, that scenario is not thread-safe and we will get inconsistent results. When a thread is already wor 5 min read
- Thread Pools in Java Background Server Programs such as database and web servers repeatedly execute requests from multiple clients and these are oriented around processing a large number of short tasks. An approach for building a server application would be to create a new thread each time a request arrives and service 9 min read
Java File Handling
- File Handling in Java In Java, with the help of File Class, we can work with files. This File Class is inside the java.io package. The File class can be used by creating an object of the class and then specifying the name of the file. Why File Handling is Required? File Handling is an integral part of any programming lan 7 min read
- Java.io.File Class in Java Java File class is Java's representation of a file or directory pathname. Because file and directory names have different formats on different platforms, a simple string is not adequate to name them. Java File class contains several methods for working with the pathname, deleting and renaming files, 6 min read
- Java Program to Create a New File A File is an abstract path, it has no physical existence. It is only when "using" that File that the underlying physical storage is hit. When the file is getting created indirectly the abstract path is created. The file is one way, in which data will be stored as per requirement. Steps to Create a N 8 min read
- Java Program to Write into a File In this article, we will see different ways of writing into a File using Java Programming language. Java FileWriter class in java is used to write character-oriented data to a file as this class is character-oriented class because of what it is used in file handling in java. There are many ways to 7 min read
- Delete a File Using Java Java provides methods to delete files using java programs. On contrary to normal delete operations in any operating system, files being deleted using the java program are deleted permanently without being moved to the trash/recycle bin. Methods used to delete a file in Java: 1. Using java.io.File.de 2 min read
- Java IO FileReader Class FileReader in Java is a class in the java.io package which can be used to read a stream of characters from the files. Java IO FileReader class uses either specified charset or the platform's default charset for decoding from bytes to characters. 1. Charset: The Charset class is used to define method 3 min read
- FileWriter Class in Java Java FileWriter class of java.io package is used to write data in character form to file. Java FileWriter class is used to write character-oriented data to a file. It is a character-oriented class that is used for file handling in java. This class inherits from OutputStreamWriter class which in turn 7 min read
- Java.io.FilePermission Class in Java java.io.FilePermission class is used to represent access to a file or a directory. These accesses are in the form of a path name and a set of actions associated to the path name(specifies which file to be open along with the extension and the path). For Example, in FilePermission("GEEKS.txt", "read" 5 min read
- Java.io.FileDescriptor in Java java.io.FileDescriptor works for opening a file having a specific name. If there is any content present in that file it will first erase all that content and put "Beginning of Process" as the first line. Instances of the file descriptor class serve as an opaque handle to the underlying machine-speci 4 min read
Java Streams and Lambda Expressions
- Lambda Expression in Java Lambda expressions in Java, introduced in Java SE 8, represent instances of functional interfaces (interfaces with a single abstract method). They provide a concise way to express instances of single-method interfaces using a block of code. Functionalities of Lambda Expression in JavaLambda Expressi 5 min read
- Method References in Java with examples Functional Interfaces in Java and Lambda Function are prerequisites required in order to grasp grip over method references in Java. As we all know that a method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller. A method can perform some specific task 9 min read
- Java 8 Stream Tutorial Java 8 introduces Stream, which is a new abstract layer, and some new additional packages in Java 8 called java.util.stream. A Stream is a sequence of components that can be processed sequentially. These packages include classes, interfaces, and enum to allow functional-style operations on the eleme 15+ min read
- Java 8 Features - Complete Tutorial Java 8 is the most awaited release of Java programming language development because, in the entire history of Java, it never released that many major features. It consists of major features of Java. It is a new version of Java and was released by Oracle on 18 March 2014. Java provided support for fu 9 min read
- Java IO : Input-output in Java with Examples Java brings various Streams with its I/O package that helps the user to perform all the input-output operations. These streams support all the types of objects, data-types, characters, files etc to fully execute the I/O operations. Before exploring various input and output streams lets look at 3 sta 6 min read
- Java.io.Reader class in Java Java Reader class is an abstract class for reading character streams. The only methods that a subclass must implement are read(char[], int, int), and close(). Most subclasses, however, will override some of the methods defined here in order to provide higher efficiency, additional functionality, or 5 min read
- Java.io.Writer Class in Java java.io.Writer class is an abstract class. It is used to write to character streams. Declaration of Writer Class in Javapublic abstract class Writer extends Object implements Appendable, Closeable, FlushableConstructors of Java Writer Classprotected Writer(): Creates a new character stream that can 6 min read
- Java.io.FileInputStream Class in Java FileInputStream class is useful to read data from a file in the form of sequence of bytes. FileInputStream is meant for reading streams of raw bytes such as image data. For reading streams of characters, consider using FileReader. Constructors of FileInputStream Class 1. FileInputStream(File file): 3 min read
- FileOutputStream in Java FileOutputStream is an outputstream for writing data/streams of raw bytes to file or storing data to file. FileOutputStream is a subclass of OutputStream. To write primitive values into a file, we use FileOutputStream class. For writing byte-oriented and character-oriented data, we can use FileOutpu 5 min read
- Ways to read input from console in Java In Java, there are four different ways to read input from the user in the command line environment(console). 1. Using Buffered Reader ClassThis is the Java classical method to take input, Introduced in JDK 1.0. This method is used by wrapping the System.in (standard input stream) in an InputStreamRe 5 min read
- Java.io.BufferedOutputStream class in Java Java.io.BufferedInputStream class in Java Java.io.BufferedOutputStream class implements a buffered output stream. By setting up such an output stream, an application can write bytes to the underlying output stream without necessarily causing a call to the underlying system for each byte written. Fie 2 min read
- Difference Between Scanner and BufferedReader Class in Java In Java, Scanner and BufferedReader class are sources that serve as ways of reading inputs. Scanner class is a simple text scanner that can parse primitive types and strings. It internally uses regular expressions to read different types while on the other hand BufferedReader class reads text from a 3 min read
- Fast I/O in Java in Competitive Programming Using Java in competitive programming is not something many people would suggest just because of its slow input and output, and well indeed it is slow. In this article, we have discussed some ways to get around the difficulty and change the verdict from TLE to (in most cases) AC. Example: Input:7 31 7 min read
Java Synchronization
- Synchronization in Java Multi-threaded programs may often come to a situation where multiple threads try to access the same resources and finally produce erroneous and unforeseen results. Why use Java Synchronization?Java Synchronization is used to make sure by some synchronization method that only one thread can access th 5 min read
- Importance of Thread Synchronization in Java Our systems are working in a multithreading environment that becomes an important part for OS to provide better utilization of resources. The process of running two or more parts of the program simultaneously is known as Multithreading. A program is a set of instructions in which multiple processes 10 min read
- Method and Block Synchronization in Java Threads communicate primarily by sharing access to fields and the objects reference fields refer to. This form of communication is extremely efficient, but makes two kinds of errors possible: thread interference and memory consistency errors. Some synchronization constructs are needed to prevent the 7 min read
- Difference Between Atomic, Volatile and Synchronized in Java Synchronized is the modifier applicable only for methods and blocks but not for the variables and for classes. There may be a chance of data inconsistency problem to overcome this problem we should go for a synchronized keyword when multiple threads are trying to operate simultaneously on the same j 5 min read
- Lock framework vs Thread synchronization in Java Thread synchronization mechanism can be achieved using Lock framework, which is present in java.util.concurrent package. Lock framework works like synchronized blocks except locks can be more sophisticated than Java’s synchronized blocks. Locks allow more flexible structuring of synchronized code. T 5 min read
- Deadlock in Java Multithreading synchronized keyword is used to make the class or method thread-safe which means only one thread can have the lock of the synchronized method and use it, other threads have to wait till the lock releases and anyone of them acquire that lock. It is important to use if our program is running in a mul 7 min read
- Deadlock Prevention And Avoidance When two or more processes try to access the critical section at the same time and they fail to access simultaneously or stuck while accessing the critical section then this condition is known as Deadlock. Deadlock prevention and avoidance are strategies used in computer systems to ensure that diffe 6 min read
- Difference Between Lock and Monitor in Java Concurrency Java Concurrency basically deals with concepts like multithreading and other concurrent operations. This is done to ensure maximum and efficient utilization of CPU performance thereby reducing its idle time in general. Locks have been in existence to implement multithreading much before the monitors 5 min read
- Reentrant Lock in Java Background The traditional way to achieve thread synchronization in Java is by the use of synchronized keyword. While it provides a certain basic synchronization, the synchronized keyword is quite rigid in its use. For example, a thread can take a lock only once. Synchronized blocks don't offer any 9 min read
- Regular Expressions in Java In Java, Regular Expressions or Regex (in short) in Java is an API for defining String patterns that can be used for searching, manipulating, and editing a string in Java. Email validation and passwords are a few areas of strings where Regex is widely used to define the constraints. Regular Expressi 8 min read
- Pattern pattern() method in Java with Examples The pattern() method of the Pattern class in Java is used to get the regular expression which is compiled to create this pattern. We use a regular expression to create the pattern and this method used to get the same source expression. Syntax: public String pattern() Parameters: This method does not 2 min read
- Matcher pattern() method in Java with Examples The pattern() method of Matcher Class is used to get the pattern to be matched by this matcher. Syntax: public Pattern pattern() Parameters: This method do not accepts any parameter. Return Value: This method returns a Pattern which is the pattern to be matched by this Matcher. Below examples illust 2 min read
- java.lang.Character class methods | Set 1 [caption id="attachment_151090" align="aligncenter" width="787"] lang.Character class wraps the value of a primitive data type - char to an object of datatype char and this object contains a single field having the data type - char. This class provides no. of methods regarding character manipulation 7 min read
- Quantifiers in Java Prerequisite: Regular Expressions in Java Quantifiers in Java allow users to specify the number of occurrences to match against. Below are some commonly used quantifiers in Java. X* Zero or more occurrences of X X? Zero or One occurrences of X X+ One or More occurrences of X X{n} Exactly n occurrenc 4 min read
Java Networking
- Java Networking When computing devices such as laptops, desktops, servers, smartphones, and tablets and an eternally-expanding arrangement of IoT gadgets such as cameras, door locks, doorbells, refrigerators, audio/visual systems, thermostats, and various sensors are sharing information and data with each other is 15+ min read
- TCP/IP Model The TCP/IP model is a fundamental framework for computer networking. It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, which are the core protocols of the Internet. This model defines how data is transmitted over networks, ensuring reliable communication between devices. It consists of 13 min read
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a Transport Layer protocol. UDP is a part of the Internet Protocol suite, referred to as UDP/IP suite. Unlike TCP, it is an unreliable and connectionless protocol. So, there is no need to establish a connection before data transfer. The UDP helps to establish low-late 10 min read
- Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6 The address through which any computer communicates with our computer is simply called an Internet Protocol Address or IP address. For example, if we want to load a web page or download something, we require the address to deliver that particular file or webpage. That address is called an IP Address 7 min read
- Difference Between Connection-oriented and Connection-less Services Two basic forms of networking communication are connection-oriented and connection-less services. In order to provide dependable communication, connection-oriented services create a dedicated connection before transferring data. On the other hand, connection-less services prioritize speed and effici 3 min read
- Socket Programming in Java This article describes a very basic one-way Client and Server setup where a Client connects, sends messages to the server and the server shows them using a socket connection. There's a lot of low-level stuff that needs to happen for these things to work but the Java API networking package (java.net) 5 min read
- java.net.ServerSocket Class in Java ServerSocket Class is used for providing system-independent implementation of the server-side of a client/server Socket Connection. The constructor for ServerSocket throws an exception if it can't listen on the specified port (for example, the port is already being used). It is widely used so the ap 4 min read
- URL Class in Java with Examples URL known as Uniform Resource Locator is simply a string of text that identifies all the resources on the Internet, telling us the address of the resource, how to communicate with it, and retrieve something from it. Components of a URL A URL can have many forms. The most general however follows a th 4 min read
- Introduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. JDBC is a Java API to connect and execute the query with the database. It is a specification from Sun Microsystems that provides a standard abstraction(API or Protocol) for Java applications to communicate with various databases. It provides the language w 6 min read
- JDBC Drivers Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the programming language Java, which defines how a client may access any kind of tabular data, especially a relational database. JDBC Drivers uses JDBC APIs which was developed by Sun Microsystem, but now this is a p 4 min read
- Establishing JDBC Connection in Java Before Establishing JDBC Connection in Java (the front end i.e your Java Program and the back end i.e the database) we should learn what precisely a JDBC is and why it came into existence. Now let us discuss what exactly JDBC stands for and will ease out with the help of real-life illustration to ge 6 min read
- Types of Statements in JDBC The Statement interface in JDBC is used to create SQL statements in Java and execute queries with the database. There are different types of statements used in JDBC: Create StatementPrepared StatementCallable Statement1. Create a Statement: A Statement object is used for general-purpose access to d 6 min read

Java Memory Allocation
- Java Memory Management This article will focus on Java memory management, how the heap works, reference types, garbage collection, and also related concepts. Why Learn Java Memory Management? We all know that Java itself manages the memory and needs no explicit intervention of the programmer. Garbage collector itself ensu 6 min read
- How are Java objects stored in memory? In Java, all objects are dynamically allocated on Heap. This is different from C++ where objects can be allocated memory either on Stack or on Heap. In JAVA , when we allocate the object using new(), the object is allocated on Heap, otherwise on Stack if not global or static.In Java, when we only de 3 min read
- Stack vs Heap Memory Allocation Memory in a C/C++/Java program can either be allocated on a stack or a heap.Prerequisite: Memory layout of C program. Stack Allocation: The allocation happens on contiguous blocks of memory. We call it a stack memory allocation because the allocation happens in the function call stack. The size of m 7 min read
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Stack Area For every thread, JVM creates a separate stack at the time of thread creation. The memory for a Java Virtual Machine stack does not need to be contiguous. The Java virtual machine only performs two operations directly on Java stacks: it pushes and pops frames. And stack for a particular thread may b 4 min read
- How many types of memory areas are allocated by JVM? JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine, In other words, it is a program/software which takes Java bytecode and converts the byte code (line by line) into machine understandable code. JVM(Java Virtual Machine) acts as a run-time engine to run Java applications. JVM is the one that actuall 3 min read
- Garbage Collection in Java Garbage collection in Java is the process by which Java programs perform automatic memory management. Java programs compile to bytecode that can be run on a Java Virtual Machine, or JVM for short. When Java programs run on the JVM, objects are created on the heap, which is a portion of memory dedica 9 min read
- Types of JVM Garbage Collectors in Java with implementation details prerequisites: Garbage Collection, Mark and Sweep algorithm Garbage Collection: Garbage collection aka GC is one of the most important features of Java. Garbage collection is the mechanism used in Java to de-allocate unused memory, which is nothing but clear the space consumed by unused objects. To 5 min read
- Memory leaks in Java In C, programmers totally control allocation and deallocation of dynamically created objects. And if a programmer does not destroy objects, memory leak happens in C, Java does automatic Garbage collection. However there can be situations where garbage collector does not collect objects because there 1 min read
- Java Interview Questions and Answers Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, known for its versatility, portability, and wide range of applications. Java is the most used language in top companies such as Uber, Airbnb, Google, Netflix, Instagram, Spotify, Amazon, and many more because of its features and per 15+ min read
- Java Multiple Choice Questions Java is a widely used high-level, general-purpose, object-oriented programming language and platform that was developed by James Gosling in 1982. Java Supports WORA(Write Once, Run Anywhere) also, it defined as 7th most popular programming language in the world. Java language is a high-level, multi- 3 min read
Java Practice Problems
- Java Programs - Java Programming Examples In this article, we will learn and prepare for Interviews using Java Programming Examples. From basic Java programs like the Fibonacci series, Prime numbers, Factorial numbers, and Palindrome numbers to advanced Java programs. Java is one of the most popular programming languages today because of it 9 min read
- Java Exercises - Basic to Advanced Java Practice Programs with Solutions Looking for Java exercises to test your Java skills, then explore our topic-wise Java practice exercises? Here you will get 25 plus practice problems that help to upscale your Java skills. As we know Java is one of the most popular languages because of its robust and secure nature. But, programmers 8 min read
- Java Quiz | Level Up Your Java Skills The best way to scale up your coding skills is by practicing the exercise. And if you are a Java programmer looking to test your Java skills and knowledge? Then, this Java quiz is designed to challenge your understanding of Java programming concepts and assess your excellence in the language. In thi 4 min read
Java Projects
- Number guessing game in Java The task is to write a Java program in which a user will get K trials to guess a randomly generated number. Below are the rules of the game: If the guessed number is bigger than the actual number, the program will respond with the message that the guessed number is higher than the actual number.If t 3 min read
- Mini Banking Application in Java In any Bank Transaction, there are several parties involved to process transaction like a merchant, bank, receiver, etc. so there are several numbers reasons that transaction may get failed, declined, so to handle a transaction in Java, there is a JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) which provides us 7 min read
- Java program to convert Currency using AWT Swing is a part of the JFC (Java Foundation Classes). Building Graphical User Interface in Java requires the use of Swings. Swing Framework contains a large set of components which allow a high level of customization and provide rich functionalities, and is used to create window-based applications. 4 min read
- Tic-Tac-Toe Game in Java In the Tic-Tac-Toe game, you will see the approach of the game is implemented. In this game, two players will be played and you have one print board on the screen where from 1 to 9 number will be displayed or you can say it box number. Now, you have to choose X or O for the specific box number. For 6 min read
- Design Snake Game Let us see how to design a basic Snake Game that provides the following functionalities: Snake can move in a given direction and when it eats the food, the length of snake increases. When the snake crosses itself, the game will be over. Food will be generated at a given interval.Asked In: Amazon, Mi 9 min read
- Memory Game in Java The Memory Game is a game where the player has to flip over pairs of cards with the same symbol. We create two arrays to represent the game board: board and flipped. The board is an array of strings that represents the state of the game board at any given time.When a player flips a card, we replace 3 min read
- How to Implement a Simple Chat Application Using Sockets in Java? In this article, we will create a simple chat application using Java socket programming. Before we are going to discuss our topic, we must know Socket in Java. Java Socket connects two different JREs (Java Runtime Environment). Java sockets can be connection-oriented or connection-less. In Java, we 4 min read
- Image Processing in Java - Face Detection Prerequisites: Image Processing in Java - Read and WriteImage Processing In Java - Get and Set PixelsImage Processing in Java - Colored Image to Grayscale Image ConversionImage Processing in Java - Colored Image to Negative Image ConversionImage Processing in Java - Colored to Red Green Blue Image C 3 min read
- Design Media Sharing Social Networking System PURPOSE OF MEDIA SOCIAL NETWORKING SERVICE SYSTEMThis system will allow users to share photos and videos with other users. Additionally, users can follow other users based on follow request and they can see other user's photos and videos. In this system, you can search users and see their profile if 14 min read
- Java Swing | Create a simple text editor To create a simple text editor in Java Swing we will use a JTextArea, a JMenuBar and add JMenu to it and we will add JMenuItems. All the menu items will have actionListener to detect any action.There will be a menu bar and it will contain two menus and a button: File menuopen: this menuitem is used 6 min read
- Java-Arrays
- java-basics
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Arrays in C – Declare, initialize and access
Array is a data structure that hold finite sequential collection of homogeneous data .
To make it simple let’s break the words.
- Array is a collection – Array is a container that can hold a collection of data.
- Array is finite – The collection of data in array is always finite, which is determined prior to its use.
- Array is sequential – Array stores collection of data sequentially in memory.
- Array contains homogeneous data – The collection of data in array must share a same data type .
We can divide arrays in two categories.
- One-dimensional array (Or single-dimensional array)
- Multi-dimensional array
Why we need arrays?
Let us understand the significance of arrays through an example.
Suppose, I asked you to write a program to input 1000 students marks from user. Finally print average of their marks .
To solve the problem you will declare 1000 integer variable to input marks. Call I/O functions to input marks in 1000 variables and finally find the average.
Think for a while how tedious will be to code if solved using above approach. Declare 1000 variables, take input in all variables, then find average and finally print its average. The above increases length of code, complexity and degrades performance. If you don’t believe, try to code solution using above approach.
To solve above problem efficiently we use arrays. Arrays are good at handling collection of data (collection of 1000 student marks). Mind that in programming, we will always use some data structure (array in our case) to handle a collection of data efficiently.
How to use arrays?
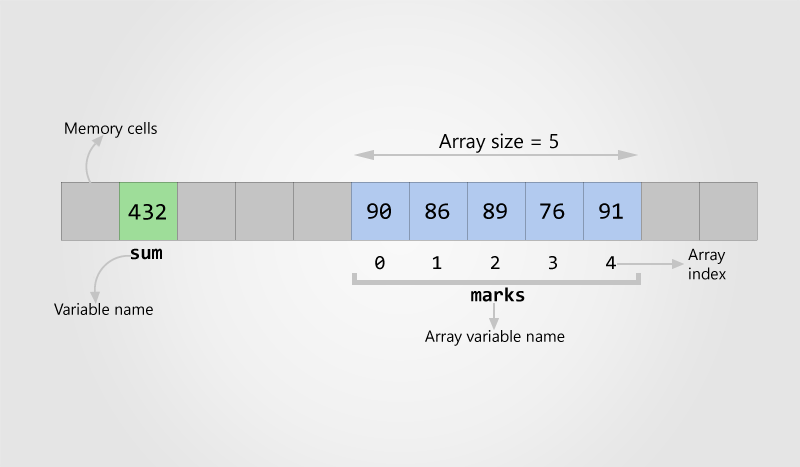
Array in memory is stored as a continuous sequence of bytes. Like variables we give name to an array. However unlike variables, arrays are multi-valued they contain multiple values. Hence you cannot access specific array element directly.
For example, you can write sum = 432; to access sum . But, you cannot access specific array element directly by using array variable name. You cannot write marks to access 4 th student marks.
In array, we use an integer value called index to refer at any element of array. Array index starts from 0 and goes till N - 1 (where N is size of the array). In above case array index ranges from 0 to 4 .
To access individual array element we use array variable name with index enclosed within square brackets [ and ] . To access first element of marks array, we use marks[0] . Similarly to access third element we use marks[2] .
How to declare an array?
Syntax to declare an array.
- data_type is a valid C data type that must be common to all array elements.
- array_name is name given to array and must be a valid C identifier .
- SIZE is a constant value that defines array maximum capacity.
Example to declare an array
How to initialize an array.
There are two ways to initialize an array.
- Static array initialization – Initializes all elements of array during its declaration.
- Dynamic array initialization – The declared array is initialized some time later during execution of program.
Static initialization of array
We define value of all array elements within a pair of curly braces { and } during its declaration. Values are separated using comma , and must be of same type.
Example of static array initialization
Note: Size of array is optional when declaring and initializing array at once. The C compiler automatically determines array size using number of array elements. Hence, you can write above array initialization as.
Dynamic initialization of array
You can assign values to an array element dynamically during execution of program. First declare array with a fixed size. Then use the following syntax to assign values to an element dynamically.
Example to initialize an array dynamically
Instead of hard-coding marks values, you can ask user to input values to array using scanf() function.
The array index is an integer value, so instead of hard-coding you can wrap array input code inside a loop .
The above code will run 5 times from 0 to 4 . In each iteration it ask user to input an integer and stores it in successive elements of marks array.
Example program to implement one-dimensional array
Let us write a C program to declare an array capable of storing 10 student marks. Input marks of all 10 students and find their average.
Output –
Array best practices
- Arrays are fixed size, hence always be cautious while accessing arrays. Accessing an element that does not exists is undefined. You may get a valid value or the program may crash.For example, consider the below program. int array[5]; // Declare an integer array of size 5 /* Accessing sixth element of array which is undefined. */ array[5] = 50; /* Accessing -1th element of array is undefined */ array[-1] = 10;
- Always keep in mind that all array element store a value of similar type.
Recommended array example programs
- Program to read and print array element.
- Program to find maximum and minimum element in array.
- Program to insert a new element in array.
- Program to search an element in array.
- Program to sort array elements.
Practice more array programming exercises to learn more.
Learn Java practically and Get Certified .
Popular Tutorials
Popular examples, reference materials, certification courses.
Created with over a decade of experience and thousands of feedback.
Java Introduction
- Get Started With Java
- Your First Java Program
- Java Comments
Java Fundamentals
- Java Variables and Literals
- Java Data Types (Primitive)
- Java Operators
- Java Basic Input and Output
- Java Expressions, Statements and Blocks
Java Flow Control
- Java if...else Statement
- Java Ternary Operator
- Java for Loop
Java for-each Loop
- Java while and do...while Loop
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java switch Statement
Java Arrays
Java Multidimensional Arrays
Java Copy Arrays
Java OOP(I)
- Java Class and Objects
- Java Methods
- Java Method Overloading
- Java Constructors
- Java Static Keyword
- Java Strings
- Java Access Modifiers
- Java this Keyword
- Java final keyword
- Java Recursion
- Java instanceof Operator
Java OOP(II)
- Java Inheritance
- Java Method Overriding
- Java Abstract Class and Abstract Methods
- Java Interface
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Encapsulation
Java OOP(III)
- Java Nested and Inner Class
- Java Nested Static Class
- Java Anonymous Class
- Java Singleton Class
- Java enum Constructor
- Java enum Strings
- Java Reflection
- Java Package
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Exceptions
- Java try...catch
- Java throw and throws
- Java catch Multiple Exceptions
- Java try-with-resources
- Java Annotations
- Java Annotation Types
- Java Logging
- Java Assertions
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Collection Interface
- Java ArrayList
- Java Vector
- Java Stack Class
- Java Queue Interface
- Java PriorityQueue
- Java Deque Interface
- Java LinkedList
- Java ArrayDeque
- Java BlockingQueue
- Java ArrayBlockingQueue
- Java LinkedBlockingQueue
- Java Map Interface
- Java HashMap
- Java LinkedHashMap
- Java WeakHashMap
- Java EnumMap
- Java SortedMap Interface
- Java NavigableMap Interface
- Java TreeMap
- Java ConcurrentMap Interface
- Java ConcurrentHashMap
- Java Set Interface
- Java HashSet Class
- Java EnumSet
- Java LinkedHashSet
- Java SortedSet Interface
- Java NavigableSet Interface
- Java TreeSet
- Java Algorithms
- Java Iterator Interface
- Java ListIterator Interface
Java I/o Streams
- Java I/O Streams
- Java InputStream Class
- Java OutputStream Class
- Java FileInputStream Class
- Java FileOutputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Class
- Java ObjectInputStream Class
- Java ObjectOutputStream Class
- Java BufferedInputStream Class
- Java BufferedOutputStream Class
- Java PrintStream Class
Java Reader/Writer
- Java File Class
- Java Reader Class
- Java Writer Class
- Java InputStreamReader Class
- Java OutputStreamWriter Class
- Java FileReader Class
- Java FileWriter Class
- Java BufferedReader
- Java BufferedWriter Class
- Java StringReader Class
- Java StringWriter Class
- Java PrintWriter Class
Additional Topics
- Java Keywords and Identifiers
- Java Operator Precedence
- Java Bitwise and Shift Operators
- Java Scanner Class
- Java Type Casting
- Java Wrapper Class
- Java autoboxing and unboxing
- Java Lambda Expressions
- Java Generics
- Nested Loop in Java
- Java Command-Line Arguments
Java Tutorials
Java Math max()
- Java Math min()
- Java ArrayList trimToSize()
An array is a collection of similar types of data.
For example, if we want to store the names of 100 people then we can create an array of the string type that can store 100 names.
Here, the above array cannot store more than 100 names. The number of values in a Java array is always fixed.
- How to declare an array in Java?
In Java, here is how we can declare an array.
- dataType - it can be primitive data types like int , char , double , byte , etc. or Java objects
- arrayName - it is an identifier
For example,
Here, data is an array that can hold values of type double .
But, how many elements can array this hold?
Good question! To define the number of elements that an array can hold, we have to allocate memory for the array in Java. For example,
Here, the array can store 10 elements. We can also say that the size or length of the array is 10.
In Java, we can declare and allocate the memory of an array in one single statement. For example,
- How to Initialize Arrays in Java?
In Java, we can initialize arrays during declaration. For example,
Here, we have created an array named age and initialized it with the values inside the curly brackets.
Note that we have not provided the size of the array. In this case, the Java compiler automatically specifies the size by counting the number of elements in the array (i.e. 5).
In the Java array, each memory location is associated with a number. The number is known as an array index. We can also initialize arrays in Java, using the index number. For example,
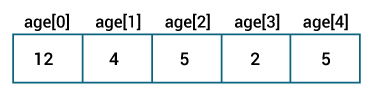
- Array indices always start from 0. That is, the first element of an array is at index 0.
- If the size of an array is n , then the last element of the array will be at index n-1 .
- How to Access Elements of an Array in Java?
We can access the element of an array using the index number. Here is the syntax for accessing elements of an array,
Let's see an example of accessing array elements using index numbers.
Example: Access Array Elements
In the above example, notice that we are using the index number to access each element of the array.
We can use loops to access all the elements of the array at once.
- Looping Through Array Elements
In Java, we can also loop through each element of the array. For example,
Example: Using For Loop
In the above example, we are using the for Loop in Java to iterate through each element of the array. Notice the expression inside the loop,
Here, we are using the length property of the array to get the size of the array.
We can also use the for-each loop to iterate through the elements of an array. For example,
Example: Using the for-each Loop
- Example: Compute Sum and Average of Array Elements
In the above example, we have created an array of named numbers . We have used the for...each loop to access each element of the array.
Inside the loop, we are calculating the sum of each element. Notice the line,
Here, we are using the length attribute of the array to calculate the size of the array. We then calculate the average using:
As you can see, we are converting the int value into double . This is called type casting in Java. To learn more about typecasting, visit Java Type Casting .
- Multidimensional Arrays
Arrays we have mentioned till now are called one-dimensional arrays. However, we can declare multidimensional arrays in Java.
A multidimensional array is an array of arrays. That is, each element of a multidimensional array is an array itself. For example,
Here, we have created a multidimensional array named matrix. It is a 2-dimensional array. To learn more, visit the Java multidimensional array .
- Java Copy Array
- Java Program to Print an Array
- Java Program to Concatenate two Arrays
- Java ArrayList to Array and Array to ArrayList
- Java Dynamic Array
Table of Contents
- Introduction
Before we wrap up, let’s put your knowledge of Java Array (With Examples) to the test! Can you solve the following challenge?
Write a function to calculate the average of an array of numbers.
- Return the average of all numbers in the array arr with the size arrSize .
- For example, if arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40} and arrSize = 4 , the expected output is 25 .
Sorry about that.
Our premium learning platform, created with over a decade of experience and thousands of feedbacks .
Learn and improve your coding skills like never before.
- Interactive Courses
- Certificates
- 2000+ Challenges
Related Tutorials
Java Tutorial
Java Library

- C Programming Tutorial
- Basics of C
- C - Overview
- C - Features
- C - History
- C - Environment Setup
- C - Program Structure
- C - Hello World
- C - Compilation Process
- C - Comments
- C - Keywords
- C - Identifiers
- C - User Input
- C - Basic Syntax
- C - Data Types
- C - Variables
- C - Integer Promotions
- C - Type Conversion
- C - Type Casting
- C - Booleans
- Constants and Literals in C
- C - Constants
- C - Literals
- C - Escape sequences
- C - Format Specifiers
- Operators in C
- C - Operators
- C - Arithmetic Operators
- C - Relational Operators
- C - Logical Operators
- C - Bitwise Operators
- C - Assignment Operators
- C - Unary Operators
- C - Increment and Decrement Operators
- C - Ternary Operator
- C - sizeof Operator
- C - Operator Precedence
- C - Misc Operators
- Decision Making in C
- C - Decision Making
- C - if statement
- C - if...else statement
- C - nested if statements
- C - switch statement
- C - nested switch statements
- C - While loop
- C - For loop
- C - Do...while loop
- C - Nested loop
- C - Infinite loop
- C - Break Statement
- C - Continue Statement
- C - goto Statement
- Functions in C
- C - Functions
- C - Main Function
- C - Function call by Value
- C - Function call by reference
- C - Nested Functions
- C - Variadic Functions
- C - User-Defined Functions
- C - Callback Function
- C - Return Statement
- C - Recursion
- Scope Rules in C
- C - Scope Rules
- C - Static Variables
- C - Global Variables
Arrays in C
- C - Properties of Array
- C - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- C - Passing Arrays to Function
- C - Return Array from Function
- C - Variable Length Arrays
- Pointers in C
- C - Pointers
- C - Pointers and Arrays
- C - Applications of Pointers
- C - Pointer Arithmetics
- C - Array of Pointers
- C - Pointer to Pointer
- C - Passing Pointers to Functions
- C - Return Pointer from Functions
- C - Function Pointers
- C - Pointer to an Array
- C - Pointers to Structures
- C - Chain of Pointers
- C - Pointer vs Array
- C - Character Pointers and Functions
- C - NULL Pointer
- C - void Pointer
- C - Dangling Pointers
- C - Dereference Pointer
- C - Near, Far and Huge Pointers
- C - Initialization of Pointer Arrays
- C - Pointers vs. Multi-dimensional Arrays
- Strings in C
- C - Strings
- C - Array of Strings
- C - Special Characters
- C Structures and Unions
- C - Structures
- C - Structures and Functions
- C - Arrays of Structures
- C - Self-Referential Structures
- C - Lookup Tables
- C - Dot (.) Operator
- C - Enumeration (or enum)
- C - Structure Padding and Packing
- C - Nested Structures
- C - Anonymous Structure and Union
- C - Bit Fields
- C - Typedef
- File Handling in C
- C - Input & Output
- C - File I/O (File Handling)
- C Preprocessors
- C - Preprocessors
- C - Pragmas
- C - Preprocessor Operators
- C - Header Files
- Memory Management in C
- C - Memory Management
- C - Memory Address
- C - Storage Classes
- Miscellaneous Topics
- C - Error Handling
- C - Variable Arguments
- C - Command Execution
- C - Math Functions
- C - Static Keyword
- C - Random Number Generation
- C - Command Line Arguments
- C Programming Resources
- C - Questions & Answers
- C - Quick Guide
- C - Cheat Sheet
- C - Useful Resources
- C - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
Arrays in C are a kind of data structure that can store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same data type . Arrays are used to store a collection of data, but it is often more useful to think of an array as a collection of variables of the same type.
What is an Array in C?
An array in C is a collection of data items of similar data type. One or more values same data type, which may be primary data types (int, float, char), or user-defined types such as struct or pointers can be stored in an array. In C, the type of elements in the array should match with the data type of the array itself.
The size of the array, also called the length of the array, must be specified in the declaration itself. Once declared, the size of a C array cannot be changed. When an array is declared, the compiler allocates a continuous block of memory required to store the declared number of elements.
Why Do We Use Arrays in C?
Arrays are used to store and manipulate the similar type of data.
Suppose we want to store the marks of 10 students and find the average. We declare 10 different variables to store 10 different values as follows −
These variables will be scattered in the memory with no relation between them. Importantly, if we want to extend the problem of finding the average of 100 (or more) students, then it becomes impractical to declare so many individual variables.
Arrays offer a compact and memory-efficient solution. Since the elements in an array are stored in adjacent locations, we can easily access any element in relation to the current element. As each element has an index, it can be directly manipulated.
Example: Use of an Array in C
To go back to the problem of storing the marks of 10 students and find the average, the solution with the use of array would be −
Run the code and check its output −
Array elements are stored in contiguous memory locations. Each element is identified by an index starting with "0". The lowest address corresponds to the first element and the highest address to the last element.

Declaration of an Array in C
To declare an array in C, you need to specify the type of the elements and the number of elements to be stored in it.
Syntax to Declare an Array
The "size" must be an integer constant greater than zero and its "type" can be any valid C data type. There are different ways in which an array is declared in C.
Declaring an Uninitialized Array
In such type of declaration, the uninitialized elements in the array may show certain random garbage values.
Example: Declaring an Array in C
In the following example, we are declaring an array of 5 integers and printing the indexes and values of all array elements −
Initialization of an Array in C
At the time of declaring an array, you can initialize it by providing the set of comma-separated values enclosed within the curly braces {}.
Syntax to Initialize an Array
If a set of comma-separated sequence values put inside curly brackets is assigned in the declaration, the array is created with each element initialized with their corresponding value.
Example to Initialize an Array
The following example demonstrates the initialization of an integer array:
Example of Initializing all Array Elements to 0
To initialize all elements to 0, put it inside curly brackets
When you run this code, it will produce the following output −
Example of Partial Initialization of an Array
If the list of values is less than the size of the array, the rest of the elements are initialized with "0".
Example of Partial and Specific Elements Initialization
If an array is partially initialized, you can specify the element in the square brackets.
On execution, it will produce the following output −
Getting Size of an Array in C
The compiler allocates a continuous block of memory. The size of the allocated memory depends on the data type of the array.
Example 1: Size of Integer Array
If an integer array of 5 elements is declared, the array size in number of bytes would be "sizeof(int) x 5"
On execution, you will get the following output −
The sizeof operator returns the number of bytes occupied by the variable.
Example 2: Adjacent Address of Array Elements
The size of each int is 4 bytes. The compiler allocates adjacent locations to each element.
In this array, each element is of int type. Hence, the 0th element occupies the first 4 bytes 642016 to 19. The element at the next subscript occupies the next 4 bytes and so on.
Example 3: Array of Double Type
If we have the array type of double type, then the element at each subscript occupies 8 bytes
Example 4: Size of Character Array
The length of a "char" variable is 1 byte. Hence, a char array length will be equal to the array size.
Accessing Array Elements in C
Each element in an array is identified by a unique incrementing index, stating with "0". To access the element by its index, this is done by placing the index of the element within square brackets after the name of the array.
The elements of an array are accessed by specifying the index (offset) of the desired element within the square brackets after the array name. For example −
The above statement will take the 10th element from the array and assign the value to the "salary".
Example to Access Array Elements in C
The following example shows how to use all the three above-mentioned concepts viz. declaration, assignment, and accessing arrays.
On running this code, you will get the following output −
The index gives random access to the array elements. An array may consist of struct variables, pointers and even other arrays as its elements.
More on C Arrays
Arrays, being an important concept in C, need a lot more attention. The following important concepts related to arrays should be clear to a C programmer −

COMMENTS
When you initialize an array, you can assign multiple values to it in one spot: int array [] = {1,3,34,5,6}; ... but what if the array is already initialized and I want to completely replace the v...
After Declaring an array we create and assign it a value or variable. During the assignment variable of the array things, we have to remember and have to check the below condition. 1. Element Level Promotion. Element-level promotions are not applicable at the array level.
We can use for loop, while loop, or do-while loop to assign the value to each element of the array. We can access any element of an array in C using the array subscript operator [ ] and the index value i of the element.
Java Arrays. Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable, instead of declaring separate variables for each value. To declare an array, define the variable type with square brackets:
In this tutorial, you will learn to work with arrays. You will learn to declare, initialize and access array elements of an array with the help of examples. An array is a variable that can store multiple values.
To declare an array in Java, use the following syntax: type [] arrayName; type: The data type of the array elements (e.g., int, String). arrayName: The name of the array. Note: The array is not yet initialized. 2. Create an Array. To create an array, you need to allocate memory for it using the new keyword:
You can assign values to an array element dynamically during execution of program. First declare array with a fixed size. Then use the following syntax to assign values to an element dynamically.
In this tutorial, we will learn to work with Java arrays. We will learn to declare, initialize, and access array elements with the help of examples. An array is a collection of similar data types.
We’ll need to start by declaring a new, larger array, and copy the elements of the base array to the second one. Fortunately, the Arrays class provides a handy method to replicate the values of an array to a new different-sized structure:
To declare an array in C, you need to specify the type of the elements and the number of elements to be stored in it. The "size" must be an integer constant greater than zero and its "type" can be any valid C data type. There are different ways in which an array is declared in C.