Theoretical Probability & Experimental Probability
Related Pages Probability Tree Diagrams Probability Without Replacement Probability Word Problems More Lessons On Probability
In these lessons, we will look into experimental probability and theoretical probability.
The following table highlights the difference between Experimental Probability and Theoretical Probability. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions.
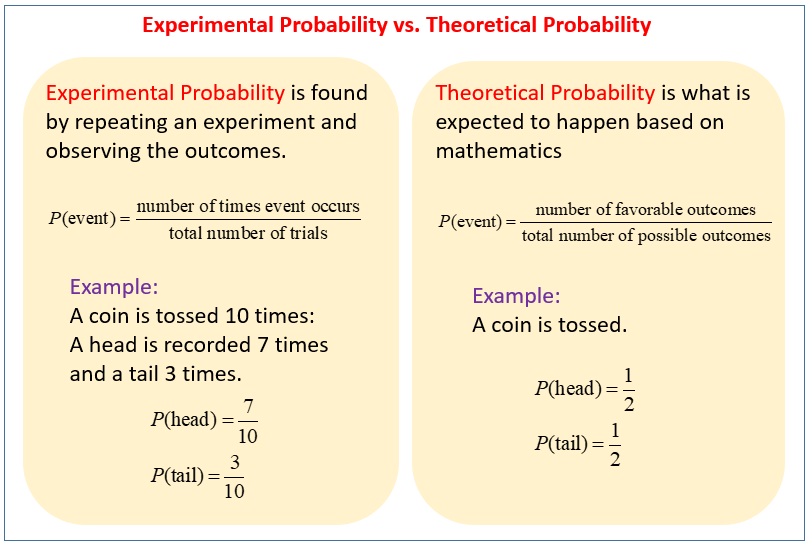
Printable Probability (Equally Likely Outcomes) Probability (Not Equally Likely Outcomes) Probability Tree Diagrams
Online Probability Problems Complementary Probability Probability Problems Probability & Geometry Mutually Exclusive Probability Independent Events Probability Dependent Events Probability

How To Find The Experimental Probability Of An Event?
Step 1: Conduct an experiment and record the number of times the event occurs and the number of times the activity is performed.
Step 2: Divide the two numbers to obtain the Experimental Probability.
How To Find The Theoretical Probability Of An Event?
The Theoretical Probability of an event is the number of ways the event can occur (favorable outcomes) divided by the number of total outcomes.
What Is The Theoretical Probability Formula?
The formula for theoretical probability of an event is
Experimental Probability
One way to find the probability of an event is to conduct an experiment.
Example: A bag contains 10 red marbles, 8 blue marbles and 2 yellow marbles. Find the experimental probability of getting a blue marble.
Solution: Take a marble from the bag. Record the color and return the marble. Repeat a few times (maybe 10 times). Count the number of times a blue marble was picked (Suppose it is 6).
How to find and use experimental probability?
The following video gives another example of experimental probability.
How the results of the experimental probability may approach the theoretical probability?
Example: The spinner below shows 10 equally sized slices. Heather spun 50 times and got the following results. a) From Heather’s’ results, compute the experimental probability of landing on yellow. b) Assuming that the spinner is fair, compute the theoretical probability of landing in yellow.
Theoretical Probability
We can also find the theoretical probability of an event.
Example: A bag contains 10 red marbles, 8 blue marbles and 2 yellow marbles. Find the theoretical probability of getting a blue marble.
Solution: There are 8 blue marbles. Therefore, the number of favorable outcomes = 8. There are a total of 20 marbles. Therefore, the number of total outcomes = 20
Example: Find the probability of rolling an even number when you roll a die containing the numbers 1-6. Express the probability as a fraction, decimal, ratio and percent.
Solution: The possible even numbers are 2, 4, 6. Number of favorable outcomes = 3. Total number of outcomes = 6
Comparing Theoretical And Experimental Probability
The following video gives an example of theoretical and experimental probability.
Example: According to theoretical probability, how many times can we expect to land on each color in a spinner, if we take 16 spins? Conduct the experiment to get the experimental probability.
We will then compare the Theoretical Probability and the Experimental Probability.
The following video shows another example of how to find the theoretical probability of an event.
A spinner is divided into eight equal sectors, numbered 1 through 8. a) What is the probability of spinning an odd numbers? b) What is the probability of spinning a number divisible by 4? b) What is the probability of spinning a number less than 3?
A spinner is divided into eight equal sectors, numbered 1 through 8. a) What is the probability of spinning a 2? b) What is the probability of spinning a number from 1 to 4? b) What is the probability of spinning a number divisible by 2?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

Before you go, check this out!
We have lots more on the site to show you. You've only seen one page. Check out this post which is one of the most popular of all time.
Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability: How do they differ?

Probability is the study of chances and is an important topic in mathematics. There are two types of probability: theoretical and experimental.
So, how to define theoretical and experimental probability? Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is based on results from experiments or surveys. In order words, theoretical probability represents how likely an event is to happen. On the other hand, experimental probability illustrates how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.
Read on to find out the differences between theoretical and experimental probability. If you wonder How to Understand Statistics Easily , I wrote a whole article where I share 9 helpful tips to help you Ace statistics.
Table of Contents
What Is Theoretical Probability?
Theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas. In other words, a theoretical probability is a probability that is determined based on reasoning. It does not require any experiments to be conducted. Theoretical probability can be used to calculate the likelihood of an event occurring before it happens.
Keep in mind that theoretical probability doesn’t involve any experiments or surveys; instead, it relies on known information to calculate the chances of something happening.
For example, if you wanted to calculate the probability of flipping a coin and getting tails, you would use the formula for theoretical probability. You know that there are two possible outcomes—heads or tails—and that each outcome is equally likely, so you would calculate the probability as follows: 1/2, or 50%.

How Do You Calculate Theoretical Probability?
- First, start by counting the number of possible outcomes of the event.
- Second, count the number of desirable (favorable) outcomes of the event.
- Third, divide the number of desirable (favorable) outcomes by the number of possible outcomes.
- Finally, express this probability as a decimal or percentage.
The theoretical probability formula is defined as follows: Theoretical Probability = Number of favorable (desirable) outcomes divided by the Number of possible outcomes.
How Is Theoretical Probability Used in Real Life?
Probability plays a vital role in the day to day life. Here is how theoretical probability is used in real life:
- Sports and gaming strategies
- Analyzing political strategies.
- Buying or selling insurance
- Determining blood groups
- Online shopping
- Weather forecast
- Online games
What Is Experimental Probability?
Experimental probability, on the other hand, is based on results from experiments or surveys. It is the ratio of the number of successful trials divided by the total number of trials conducted. Experimental probability can be used to calculate the likelihood of an event occurring after it happens.
For example, if you flipped a coin 20 times and got heads eight times, the experimental probability of obtaining heads would be 8/20, which is the same as 2/5, 0.4, or 40%.
How Do You Calculate Experimental Probability?
The formula for the experimental probability is as follows: Probability of an Event P(E) = Number of times an event happens divided by the Total Number of trials .
If you are interested in learning how to calculate experimental probability, I encourage you to watch the video below.
How Is Experimental Probability Used in Real Life?
Knowing experimental probability in real life provides powerful insights into probability’s nature. Here are a few examples of how experimental probability is used in real life:
- Rolling dice
- Selecting playing cards from a deck
- Drawing marbles from a hat
- Tossing coins
The main difference between theoretical and experimental probability is that theoretical probability expresses how likely an event is to occur, while experimental probability characterizes how frequently an event occurs in an experiment.
In general, the theoretical probability is more reliable than experimental because it doesn’t rely on a limited sample size; however, experimental probability can still give you a good idea of the chances of something happening.
The reason is that the theoretical probability of an event will invariably be the same, whereas the experimental probability is typically affected by chance; therefore, it can be different for different experiments.
Also, generally, the more trials you carry out, the more times you flip a coin, and the closer the experimental probability is likely to be to its theoretical probability.
Also, note that theoretical probability is calculated using mathematical formulas, while experimental probability is found by conducting experiments.
What to read next:
- Types of Statistics in Mathematics And Their Applications .
- Is Statistics Harder Than Algebra? (Let’s find out!)
- Should You Take Statistics or Calculus in High School?
- Is Statistics Hard in High School? (Yes, here’s why!)
Wrapping Up
Theoretical and experimental probabilities are two ways of calculating the likelihood of an event occurring. Theoretical probability uses mathematical formulas, while experimental probability uses data from experiments. Both types of probability are useful in different situations.
I believe that both theoretical and experimental probabilities are important in mathematics. Theoretical probability uses mathematical formulas to calculate chances, while experimental probability relies on results from experiments or surveys.
I am Altiné. I am the guy behind mathodics.com. When I am not teaching math, you can find me reading, running, biking, or doing anything that allows me to enjoy nature's beauty. I hope you find what you are looking for while visiting mathodics.com.
Recent Posts
How to Find the Y-Value of Stationary Points with TI-84 Plus CE
TI-84 Plus CE Calculator If you’re studying calculus or any advanced math course, you will certainly come across the concept of stationary points. So, what is a stationary point? A...
IB Maths Vs. A-Level Maths - Which One is Harder?
Maths is a subject that can be demanding for many students. It not only requires strong analytical skills but also an ability to handle complex concepts with ease. Students looking to further their...
