- Physics Article
- To Determine Refractive Index Of A Glass Slab Using A Travelling Microscope

To Determine Refractive Index of a Glass Slab Using a Travelling Microscope
A Travelling microscope is a compound microscope that is fitted on a vertical scale. It carries a vernier scale along the main scale and can be moved upward or downward. Below is an experiment to determine refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
To determine the refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
Materials Required
- 3 glass slabs of different thicknesses but the same material
- A travelling microscope
- Lycopodium powder
The principle behind glass slab
When a glass slab is placed on a horizontal surface, and its bottom surface is viewed from the top, it appears to be elevated due to refraction. The apparent thickness of the slab is determined by the distance between the apparent bottom and the top of the glass slab. The refractive index with respect to the medium and air is given as:
Read More: Refractive Index
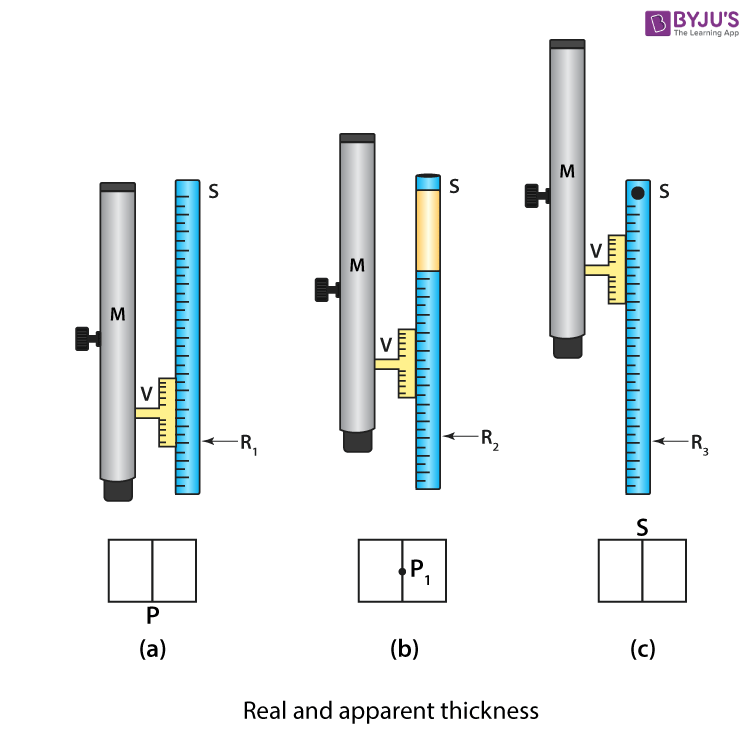
Adjustment of a travelling microscope
- To get sufficient light, place the travelling microscope (M) near the window.
- To make the base of the microscope horizontal, adjust the levelling screw.
- For clear visibility of the cross wire, adjust the position of the eyepiece.
- For the vertical scale of the microscope, determine the vernier constant.
- Mark point P on the microscope’s base using black ink.
- To avoid the parallax between the cross-wires and the mark P, make the microscope vertical and focus on P.
- Let R 1 be the vernier scale and main scale reading on the vertical scale.
- Place the glass slab with the least thickness over the mark P.
- Let P 1 be the image of the cross mark. Move the microscope upwards and focus on P 1 .
- For reading, R 2 on the vertical scale repeat step 7.
- Sprinkle a few particles of lycopodium powder on the slab’s surface.
- To focus the particle near S, raise the microscope further upward.
- For reading, R 3 on the verticle scale repeat step 7.
- Repeat the above steps for different thickness glass slabs.
- Record the observations.
Observations and Calculations
Vernier constant for the vertical scale of microscope = ……..cm
Table for microscope readings
The ratio \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{R_{3}-R_{1}}{R_{3}-R_{2}}\end{array} \) is constant and gives the refractive index of the glass slab.
Precautions
- The parallax in a microscope should be removed properly.
- To avoid backlash error, the microscope should be moved upward.
Sources Of Error
- The scale used in the microscope might not be calibrated properly.
- The lycopodium powder layer on the glass slab might be thick.
Viva Questions
Q1. Define normal shift.
Ans: Normal shift is defined as the difference between actual depth and apparent depth.
Q2. What causes a normal shift?
Ans: Normal shift is caused due to the refraction of light.
Q3. What is the SI unit of normal shift?
Ans: The SI unit of normal shift is a metre.
Q4. What is apparent shift?
Ans: Apparent shift is defined as the difference between the object’s distance from the refracting surface and the image distance from the refracting surface.
Q5. On what factors does the apparent depth depend?
Ans: Following are the factors on which the apparent depth depend:
- Nature of the medium
- Thickness of medium
- Colour of light
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about other Physics-related experiments.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Physics related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
To determine the refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
Home Experient 15
Class 12 Physics Practicals List
To determine the angle of minimum deviation for a given glass prism by plotting a graph between angle of incidence and the angle of deviation.
To determine resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method.
To determine resistance per cm of a given wire by plotting a graph of potential difference verses current.
To find the value of V for different values of u in case of a concave mirror and to find the focal length.
To find the refractive index of a liquid (water) using a concave mirror.
To compare the e.m.f. of the given primary cells (Daniel and Leclanche) using a potentiometer.
To find the focal length of a convex lens by plotting graph.
To determine the internal resistance of a given primary cell by using potentiomenter.
To find resistance of a given wire using meter bridge and hence determine the specific resistance of its material.
To verify the laws of combination (series/parallel) of resistance using a meter bridge.
To convert the given galvanometer into an ammeter of desired range and verify the same.
To convert the given galvanometer into a voltmeter of desired range and verify the same.
To draw I-V characteristic curve of a p-n junction in forward bias and reverse bias.
To draw the characteristic of a zener diode and to determine its reverse breakdown.
To assemble a household circuit comparing three bulbs, three (on - off) switches, a free a power source.
To assemble the component of a given electric circuit
To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit between sharp edges of major blades.
To observe the polarisation of light using two polaroids.
To identify a diode, and LED, a transistor, integrated circuit (IC), a resistor and a capacitor from a mixed collection.
To study the size and nature of the image formed by a concave mirror using a candle and a screen (for different distances of the candle from the mirror.)
To design an appropriate logic gate combination for a given truth table.
Test Preparation
- Mathematics
Quick Links
- Advertise With Us
- Online Examination Section
- CBSE Sample Paper Download
- School Projects Download
- Model Sample Papers Download
- Class 12 Practicals with Solutions
- Student Solutions
- Teacher Solutions
- Corporate Solutions
Social Platform
Online courses.
- Other Competative Exams
© 2017 Knowledge Universe Online All rights are reserved

- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Free Video Lectures
- CBSE Important Questions
- CBSE Objective (MCQs)
- Assertation & Reasoning Questions
- Case Study Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample paper
- CBSE Mock Test Paper
- Question Bank
- Project, Practical & Activities
- ICSE Free Video Lectures
- Class 6 ICSE Revision Notes
- CLASS 7 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 8 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 9 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- CLASS 10 ICSE REVISION NOTES
- Class 6 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 7 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 8 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 9 ICSE Solutions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Solutions
- Class 6 ICSE Important Questions
- CLASS 7 ICSE Important Question
- CLASS 8 ICSE IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
- CLASS 9 ICSE Important Questions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Important Question
- Class 6 ICSE Mcqs Question
- Class 7 ICSE Mcqs Question
- CLASS 8 ICSE MCQS QUESTION
- CLASS 9 ICSE Mcqs Questions
- CLASS 10 ICSE Mcqs Question
- ICSE Syllabus
- Class 6th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 7th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 8th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 9th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 10th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 11th Quick revision Notes
- Class 12th Quick Revision Notes
- Class 6th NCERT Solution
- Class 7th NCERT Solution
- Class 8th – NCERT Solution
- Class 9th NCERT Solution
- Class 10th NCERT Solution
- Class 11th NCERT Solution
- Class 12th NCERT Solution
- Class 6th Most Important Questions
- Class 7th Important Questions
- Class 8th Important Questions
- Class 9th Most Important Questions
- Class 10th Most Important Questions
- Class 11th important questions
- Class 12th important questions
- Class 6th MCQs
- Class 7th MCQs
- Class 8th MCQs
- Class 9th MCQs
- Class 10th MCQs
- Class 11th MCQs questions
- Class 12th Important MCQs
- Case Based Questions
- NCERT Books in Pdf
- NCERT Chapter Mind Maps
- OliveTree Books Study Materials
- Forever With Books Study Material
- Rs Aggrawal Solutions
- RD Sharma Solution
- HC Verma Solution
- Lakhmir Singh Solution
- T.R Jain & V.K ohri Solution
- DK Goel Solutions
- TS Grewal Solution
- Our Products
- Edugrown-Candy Notes & Solution
- Online Tuition Services
- Career Advisor Booking
- Skill Development Courses
- Free Video Lectures
- Mock Test Papers
To determine the refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope | Cbse Class 12th physics practical
- Class 12th PCMB
- To determine the refractive index…
Table of Contents
To determine the refractive index of glass by using travelling microscope.
Apparatus required
A travelling microscope with vernier scale, a glass slab, white paper, a pen and lycopodium powder.
Formula Used

Observations
1. Least count of main scale of microscope = 0.5 mm.
2. Number of division on vernier scale=50

Calculation

The refractive index of the glass slab by using travelling microscope = 1.48
PRECAUTIONS
- Microscope once focussed on the cross-mark, the focussing should not be disturbed throughout the experiment. Only rack and pinion screw should be used to raise the microscope upward.
- Only a thin layer of lycopodium powder should be spread on the top of the slab.
- The microscope tube should be vertical.
- Microscope should not be shaky.
- Eyepiece should be adjusted so that cross-wires are distinctly seen.
- As far as possible, the rack and pinion screw should be moved in one direction only to avoid backlash error.
SOURCES OF ERROR
- The scale used in the microscope might be caliberation property.
- Microscope tube may not be exactly vertical.
- The lycopodium powder layer on the glass slab might be thick.
Share this:
Discover more from edugrown school.
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
Author: school
Related posts.
Class 12th Physics Model Sample Paper For CBSE Board Exam with Solution Set-4 Full Syllabus October 21, 2024
Class 12th Physics Model Sample Paper For CBSE Board Exam with Solution Set-3 Full Syllabus October 21, 2024
Class 12th Physics Model Sample Paper For CBSE Board Exam with Solution Set-2 Full Syllabus October 21, 2024
Class 12th Physics Model Sample Paper For CBSE Board Exam with Solution Set-1 Full Syllabus October 21, 2024

To find the refractive index of a liquid using a convex lens and plane mirror | cbse class 12th physics practical October 1, 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Post comment
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- About Contact Sing up Log in
- Business & Industries
- Shipping & Logistics
- Markets & Trading
- Finance & Loan
- Automobiles
- Cryptocurrency
- Beauty & Skin Care
- Gift & Jewellery
- Pets & Animals
- Software & Web Development
- Digital Marketing
- Latest Technologies
- Education & Training
- Jobs & Career
- Health & Fitness
- Medical & Health
- Sports & Athletics
To determine the refractive index of a glass using travelling microscope
To determine the refractive index of a glass using travelling microscope.
A marker, glass slab, travelling microscope, lycopodium powder.

Formulae Used:
The refractive index, μ= real depth /apparent depth = r 3 -r 1 /r 2 -r 1
Observations:
Least count of travelling microscope = 0.001 cm or 0.01 mm Mean values: r 1 = 0 mm r 2 = 6.81 mm r 3 = 10.25 mm
Observations: Reading of Microscope focused on:
Calculations:.
Real depth = d r = r 3 – r 1 = Mean d r = 10.25 mm
Apparent depth = d a = r 2 – r 1 1
Mean d a = 6.81 mm
∴ Refractive index, μ = real depth /apparent depth = d r /d a ∴μ= 1.52
The refractive index of the glass slab by using travelling microscope is determined as 1.52=μ
Precautions:
- Microscope once focused on the cross mark, the focusing should not be disturbed throughout the experiment. Only rack and pinion screw should be turned to move the microscope upward.
- Only a thin layer of powder should be spread on top of slab.
- Eye piece should be so adjusted that cross-wires are distinctly seen.

Latest Post

Fashion for Fit Bodies: Expert Styling Tips to Flaunt Your Six Pack Abs

Top 8 Female Casino Streamers Making Waves in 2024

Kirill Yurovskiy: How to Calculate Travel Time

Mastering Pool Cleaning Robot Safety and Efficiency: Your Essential Guide

E-Sports and Betting: The Perfect Match for the Digital Age

Timur Turlov: Visionary Entrepreneur and Advocate for Financial Innovation

How to Use Futures and Options for Hedging Strategies
Related categories.
- Class 12 Physics
- Engineering Physics
- Class 11 Physics
- Physics Knowledge Base
- Physics Class 10
Class 12 Physics Lab Experiment list
- 1 To find resistance of a given wire using Whetstone’s bridge (meter bridge)
- 2 To find the focal length of a convex mirror using a convex lens
- 3 To find the value of ‘v’ for different values of ‘u’ in case of a concave mirror & to find its focal length
- 4 To draw the characteristics curves of a zener diode vs to determine its reverse breakdown voltage
- 5 To find the focal length of a concave lens using a convex lens
- 6 To verify the laws of combination (series & parallel) of resistances using meter bridge (slide Wire Bridge)
- 7 To determine the refractive index of a glass using travelling microscope
Laboratory Experiment Categories
- Electrical and Electronics
- Civil Engineering
- Engineering Mechanics
- Mechanical Engineering
- Biomedical Engineering
Get all latest content delivered to your email a few times a month.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- Competency Based Questions
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- LPU Mock Test
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- NEET Toppers Notes
- NEET Formula
- NEET Important Question
- NEET Assertion Reason Question
- NEET Study Planner
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Refractive Index of Prism Material Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Physics Lab Manual Class 12
Free pdf download.
SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
There is no mode of learning better than learning from practical knowledge and that is why CBSE has prescribed students the Lab Manual of Class 12 Physics Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid. Students looking for an individual file of Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Physics Lab Manual Class 12 can use the link we have provided here on this page.
Interestingly, the PDF file not only contains the process to perform an activity on the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid but helps students prepare for the internal assessment and Viva examination.
What Includes Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual Class 12 PDF?
Inside the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual Class 12 PDF, there are various helpful and important things for students - Discussed below in detail:
- Quick Revision Notes: To quickly recap the concepts of the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid the PDF file of CBSE Class 12 Lab Manual Physics contains short notes to refresh the learning of students before performing the activity.
- Aim: The purpose of the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid activity is mentioned in the Aim section. It helps students understand what should be the final result of this laboratory activity.
- Materials Required: All the apparatus required to perform the practical activity on the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid is mentioned in this section.
- Theory: The theory section explains the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid in a little short brief to give students an initial idea of the topic to perform the activity given in the lab manual.
- Graphics/Images/Illustrations: To help students better understand the process or some of the apparatus, the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Physics Lab Manual Class 12 contains images, graphs and illustrations.
- Procedure: This section includes, a stepwise guide to help students to perform the activity on the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid.
- Observations: The observed data extracted from performing the activity on the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid is mentioned in this section.
- Precautions: One of the crucial things while conducting the activity given in Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid lab manual is to take precautions to avoid making mistakes or getting hurt. The precautions section in the lab manual explains students to what to not do during the activity of Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid.
- Source of Error: The PDF that we provide contains, the source of error that help students understand the cause of not getting the desired outcome.
Where to Download Lab Manual of CBSE Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid?
Always choose a trustworthy platform to download study materials such as Selfstudys.com. If you want to download the PDF file of Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid from Selfstudys then follow the steps given below:
- Navigate to the website (Selfstudys.com) on any internet browser
- Once, the website loads, tap on the navigation button
- Tapping on the navigation button will give you further options to choose from - Again, tap on CBSE
- In this step, you are required to tap or click on Lab Manual
- A new page will open, choose Class 12 and then click on Physics to access the PDF file of Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual of CBSE Class 12.
What is the Significance of the Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual?
From helping students perform the practical activity to preparing for the annual Viva examination, the Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual plays a significant role in a student’s academic session. Here are some of the key significant roles:
- Helps Prepare Practical Notebook: For internal assessment, students must prepare the practical notebook of Class 12 Physics and while preparing the practical notebook the Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual PDF can help students. It can help because it works like a guidebook.
- Assistance in Practising Viva Questions: The PDF file of the Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual we provide contains Viva questions along with some extra MCQ types of questions. Thus, here, the Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual helps students practice Viva questions to be ready for the upcoming annual examination.
- Helps Develop a Better Command of Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid: By helping students practice activities mentioned in the Class 12 Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid Lab Manual, it enables them to develop a better and stronger command of the topics and concepts covered.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

"Log in, submit answer and win prizes"

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

"Enter your details to claim your prize if you win!"
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Determine Refractive Index of a Glass Slab using a Travelling Microscope

Refractive Index of a Glass Slab
Objective: We will design a system to measure the refractive index of a glass slab using a moving microscope.
Introduction: A glass slab is a piece of glass with thickness ranging from a few millimeters to several meters. The refractive index of a glass slab is the ratio of the index of refraction to the thickness of the glass. Measurement of the refractive index of glass is important for optical applications like optical fiber and photonic crystal.
Structure: There are various methods for measuring the refractive index. We will measure the refractive index using a moving microscope.
Step 1: What will we need?
( Note: the same items are also required to create a light microscope)
We will start the design by looking for an item that can be used as both a lens and a holder. The most ideal item would be a microscope lens since we can use it to focus light on the glass slab and to measure the distance. We can also use it as a holder if we have to insert another lens to take a refractive index measurement.
We can use a microscope lens holder to attach the microscope lens in place. The microscope lens we will use is called an objective lens. The objective lens has a central convex lens that magnifies an object to be magnified.
Since the lens holder is circular, we can make the convex lens circular. We can use a microscope objective lens as a holder because the thickness of the lens holder is quite small.
We can buy the lens holder at a local store. However, we may have to make it from scratch. We will need a microscope, a microscope objective lens, a stepper motor, a potentiometer, and an Arduino board. We will describe the building process in the next section.
Step 2: Building process
Step 2.1: Choosing a Microscope
We should buy a microscope to work with. First, we should consider the following when we are buying a microscope.
Whether it is a microscope made in a lab or one in a store. Amount of microscope that we want to buy. What brand name is most popular in stores, but can be bought for a cheaper price Next, we should decide where to mount the microscope. We should decide the size of the slab.
Also, if we use the same microscope for different experiments, we should decide whether we should buy a holder that can hold different lenses. If so, which size is most convenient?
Also, a microscope has to be able to magnify the object we are measuring the refractive index. We can decide whether the microscope has a magnification of 1x, 4x, 10x, 20x, and 40x.
2.1.1 Choosing a microscope
You can buy a microscope in the market.
Or, if you don't want to buy one, then you can ask your teacher for help. In any case, we can choose a microscope of the following three types.
Microscope made in a laboratory
Microscope made in a store
Electron microscope
Now we will start the buying process.
Microscope Made in a Lab
The easiest way to start the process of buying a microscope is to ask your teacher to help. In this case, your teacher is going to give you instructions on buying a microscope for your experiments. There are many types of microscopes. Your teacher will give you some instructions.
Microscopes Made in a Store
If you don't have enough money to buy the microscope made in a laboratory, then you can buy one in a store. First, you have to buy the microscope itself. To do this, you have to visit a store of the type you want. Once you have seen the types of microscopes, the price of each one, and its functions, you will be able to choose the microscope that you need.
Electron Microscope
An electron microscope is an extremely high-tech microscope. We can't get an electron microscope at home. We have to find the store of the type we want to buy.
The advantage of an electron microscope over a general microscope is the resolution. We can obtain the magnification of the electron microscope of a hundred thousand times the magnification of the microscope we normally use. There are many types of electron microscopes. You have to find the store of the type you want to buy.
How to Do a Test With a Microscope?
There are two methods to test how the microscope works:
Direct Observation
When you test a microscope, you have to place an object in the objective lens, which is the lens where we'll see the object. The objective lens is very big, so it is not possible to directly observe its function from the camera. You have to buy a microscope with a camera. If you have bought a microscope, you can test its performance by looking at an object through the objective lens.
In this way, you can test if you can correctly see the object you are going to use. It is easier to take pictures with a small lens. For example, it is easier to take a test with the 30X objective, and it is difficult to do a test with the 400X objective. It is better to test an objective lens that has a strong lens.
Test With an Object that You Already Have
If you already have an object, it is easy to test the working principle of a microscope. However, it is not easy to test the microscope's performance in this way. In this case, you have to find an object that has sharpness and contrast.
What is Sharpness?
If the object that you want to observe has sharpness, you can better observe its details. If there is no sharpness, you cannot observe the fine details of the object. There are many kinds of sharpness in the object, such as
Line (edge sharpness)
Curve (curve sharpness)
Point (dots sharpness)
There are also different types of sharpness in the observer's eyes, but this is not very important.
What is Contrast?
If the object that you want to observe has contrast, the edges of the object will be very clear and the objects can be distinguished. When you observe an object, it will be bright and dark, and we can judge whether the object is soft or hard. However, sometimes the object is not bright, and then it will be difficult to see the contrast.
How to test the Microscope?
You must try to find an object that has sharpness and contrast. If you do not find such an object, then you can buy one from a supermarket.
You can also refer to the specification of the microscope. First, make sure that you are familiar with how the microscope works. Second, make sure that you understand what a working principle means. If you are not familiar with a working principle, you must refer to the documentation. If you think it is appropriate, you can buy a kit or assemble the kit yourself. Third, we will learn how to use the microscope.
You must put a microscope slide (a white plate), a cover glass, a mirror, a camera lens, a light source, a tripod, a flashlight, a microscope, a micro-adjustment tool, a slide pen, and an adhesive tape in front of you.
Students often face trouble while conducting a travelling microscope experiment. Here, we will discuss the correct procedure to conduct this experiment, ensuring the best possible outcome.
However, before proceeding with the travelling microscope experiment class 12, let us learn some of the important factors necessary for the same.
Defining Refractive Index
Index of refraction, or refractive index is defined as the measure of the deviation of a light ray when it passes from one medium to another. In simpler terms, suppose you have a glass full of water. If you place it in sunlight, the light bends upon entering the water. If you measure the angle of such a bend, you will get its refractive index.
You can calculate a refractive index if the velocity of light c for a particular wavelength in empty space is known. Additionally, you must also know the value of ‘v’, which represents light’s velocity in a substance. In such a case, refractive index n = c/v
What is a Travelling Microscope?
Before you can use a travelling microscope experiment effectively, you must understand the functionality of such a device. Travelling microscopes act as simple microscopes, with one exception.
Where a simple microscope remains fixed for the duration of a study or experiment, a travelling microscope’s head is fitted onto a slider. Therefore, it can move along a scale, studying an object from various distances. Readings are taken by combining the readings from the Vernier and main scale.
Now, let us proceed to determine the refractive index of the glass slab using a travelling microscope.
Apparatus Necessary
Three glass slabs, each varying in thickness. Material for each slab must be identical.
Travelling microscope, and
Lycopodium powder
Theory for Refractive Index Experiment Report
Refractive Index (n) = Slab’s real thickness/slab’s apparent thickness
Procedure to Follow
To ensure accuracy in this refractive index of a glass slab using travelling microscope readings, follow the process mentioned below.
Step 1: Place a travelling microscope near a light source.
Step 2: Adjust screws to ensure that the base of this microscope is horizontal.
Step 3: Position the microscope horizontally, check the eyepiece to see whether the cross wires are visible clearly.
Step 4: Check the Vernier Constant of this scale when it is kept vertically.
Step 5: Use a marker to draw a mark at the microscope’s base. Consider this point as P.
Step 6: Now, focus the vertical microscope on point P in such a way that there is no chance of parallax between this image of P and the cross wires.
Step 7: Now, note the vernier scale, as well as the main scale reading. Consider this as R 1 .
Step 8: Place the thinnest glass slab on point P.
Step 9: Lift the microscope and focus the image of P 1 of the cross-mark.
Step 10: Make a note of the reading on the vertical scale (R 2 ).
Step 11: Sprinkle lycopodium powder on the slab.
Step 12: Lift the microscope further, focusing it on this particle near S.
Step 13: Make a note of R 3 on this vertical scale.
Step 14: Follow the same procedure to take readings of the other glass slabs.
Note down the results in a tabular format for increased ease of calculations.
Table for Readings
Refractive Index Calculation = R3 – R1/R3 – R2
Mean Refractive Index = n1 + n2 + n3/3
Precaution- Ensure that you remove the parallax properly in step 6, failing which results of this travelling microscope experiment can be erroneous.
To know more about refractive index and experiments in general, consult our live online classes. Our experienced teachers guide you toward proper understanding with an expertly devised curriculum. Furthermore, now you can also download our Vedantu app for added convenience.
FAQs on Determine Refractive Index of a Glass Slab using a Travelling Microscope
1. How can I define a normal shift?
Normal shift is nothing but the difference between actual depth and apparent depth of an image.
2. What is the refractive index of a glass slab, which is hollow?
For such a glass, the refractive index or n is always 1.
3. What is the significance of lycopodium powder in this experiment?
Lycopodium powder ensures that the microscope’s focus is correct, and not at this bottom surface of this transparent slab.
4. Where can I find notes on the Refractive Index?
Students often face trouble while conducting a travelling microscope experiment. Here, we will discuss the correct procedure to conduct this experiment, ensuring the best possible outcome. Vedantu is a platform that aims at making students well prepared for the final exams and therefore it provides notes and answers to all the questions of previous year question papers obtained from expert teachers in the subject which can be downloaded either through the app or website.
5. Is physics tough?
Class 10 Physics consists of 10 interesting chapters which are all important in the field of physics as they lay the foundation for many diverse topics in further levels of education. Students panic due to the vast syllabus which results in stress and poor performance in exams. Preparing physics could be as easy yet interesting as playing your favorite game if the concepts are divided into small topics and experiments which could be practically done. Therefore physics isn’t tough but interesting provided proper attention is given.

NCERT Study Material

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This instrument is used to determine the refractive index of the glass slab. Login. Study Materials. ... It carries a vernier scale along the main scale and can be moved upward or downward. Below is an experiment to determine refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope. ... Physics Experiments Class 12 Viva Questions and ...
EXPERIMENT AIM To determine refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED A travelling microscope, a glass slab, lycopodium powder/chalk dust and a paper. 141414 Fig. E 14.1 Formation of image I of a point 0 in a glass slab PRINCIPLE If a glass slab is placed in air on a horizontal surface and ...
Physics Class 12 model, CBSE Papers, 2016 with solutions Physics & Chemistry Class 12 Practical Solutions for CBSE Board Examinations by Dr. Mukesh Shrimali To determine the refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
Objective To determine the refractive index of glass by using travelling microscope. Apparatus required A travelling microscope with vernier scale, a glass slab, white paper, a pen and lycopodium powder. Formula Used Diagram Observations 1. Least count of main scale of microscope = 0.5 mm. 2. Number of division on vernier scale=50 Calculation Result The…
We are grateful to the teachers for their constant support provided in the preparation of this CBSE Class 12 Lab Manual. CBSE Class 12 Lab Manual for Chapter 9 3 To Determine Refractive Index of a Glass Slab Using a Travelling Microscope. The laboratory is important for making the study complete, especially for a subject like Science and Maths.
∴ Refractive index, μ = real depth /apparent depth = d r /d a ∴μ= 1.52. Result: The refractive index of the glass slab by using travelling microscope is determined as 1.52=μ. Precautions: Microscope once focused on the cross mark, the focusing should not be disturbed throughout the experiment.
The following is an experiment utilising a travelling microscope to determine the refractive index of a glass slab. The refractive index is a measurement of how far a light ray deviates when it pauses between two materials. It's a one-dimensional integer that determines the speed of light. The refractive index is defined as the ratio of light ...
The use of the Class 12 Lab Manual for Class 12 Physics Refractive Index of Prism Material, Glass Slab and Transparent Liquid can benefit students in a variety of ways such as in the annual exam preparation, internal assessment, project work, Viva voce and more.
Theory for Refractive Index Experiment Report. Refractive Index (n) = Slab's real thickness/slab's apparent thickness. Procedure to Follow. To ensure accuracy in this refractive index of a glass slab using travelling microscope readings, follow the process mentioned below. Step 1: Place a travelling microscope near a light source.
EXPERIMENT-01 REFRACTION THROUGH GLASS SLAB AIM: To trace the course of different rays of light through a rectangular glass slab at different angles of incidence, measure the angle of incidence, refraction and verify Snell`s law. Also measure the lateral displacement. APPARATUS: Drawing board, sheet of paper, board pins, rectangular glass slab.